
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1740757
商業宇宙打上げの市場機会、成長促進要因、産業動向分析、2025年~2034年予測Commercial Space Launch Market Opportunity, Growth Drivers, Industry Trend Analysis, and Forecast 2025 - 2034 |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
|
|||||||
| 商業宇宙打上げの市場機会、成長促進要因、産業動向分析、2025年~2034年予測 |
|
出版日: 2025年04月24日
発行: Global Market Insights Inc.
ページ情報: 英文 190 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
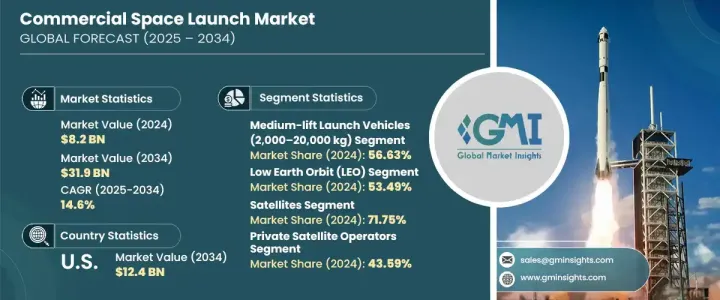
世界の商業宇宙打上げ市場は、2024年には82億米ドルと評価され、CAGR14.6%で成長し、2034年には319億米ドルに達すると予測されています。
この爆発的な成長は、宇宙技術の急速な進歩、打上げサービスの低価格化、接続性、地球観測、科学研究に対する需要の高まりに後押しされています。世界の宇宙経済は、商業企業がより活発で影響力を持つようになり、かつては政府主導の分野であったものが、競争力のあるイノベーション主導の産業へと変貌を遂げ、根本的な変化を遂げつつあります。衛星の小型化と製造コストの削減により、民間や機関投資家による宇宙へのアクセスが容易になりました。
低軌道衛星コンステレーション、気象モニタリング、リアルタイムイメージング、次世代通信への関心が高まる中、商業宇宙打上げ部門は、より広範な航空宇宙エコシステムの重要な柱へと発展しています。宇宙経済が従来の探査にとどまらず多様化するにつれて、データサービス、衛星間リンク、宇宙ベースのインフラストラクチャーなどのビジネスチャンスが新たなフロンティアを開き続けています。世界各国は打上げインフラ、規制改革、研究開発に多額の投資を行っており、新興諸国市場は資本と人材の両方にとって魅力的な市場となっています。
| 市場範囲 | |
|---|---|
| 開始年 | 2024 |
| 予測年 | 2025-2034 |
| 開始金額 | 82億米ドル |
| 予測金額 | 319億米ドル |
| CAGR | 14.6% |
小型衛星打上げの需要は、通信、地球画像、気候追跡、科学実験など広範な機能に対応する小型ペイロードの配備の実現可能性が高まったために急増しています。より小型の衛星をより頻繁に、かつ手頃な価格で打ち上げる能力は、民間企業にとっても政府機関にとっても画期的なことです。この変革は、打ち上げコストの大幅な削減と費用対効果の高い小型化技術の導入によって加速しています。
その結果、企業は軌道プラットフォームへのアクセスが拡大し、革新的な衛星サービスの迅速な展開が可能になりました。打上げ事業への民間セクターの参入の増加は、政府の支援政策やライセンシング手続きの合理化と相まって、世界の宇宙打上げエコシステムを再構築しています。増加する商業ミッションの量と種類をサポートするため、専用打上げ場や地域宇宙港の開発が進んでいます。このような拡大は、機関投資家や商業顧客の裾野を広げ、打上げ頻度の急増に寄与しています。
しかし、地政学的な貿易摩擦と変動する国際政策が、業界のコスト構造に複雑さを加えています。航空宇宙部品や推進システムへの輸入関税は、サプライチェーンを混乱させ、製造コストを上昇させています。こうしたリスクを軽減するため、企業は生産を現地化し、材料を国内で調達する方向に動いています。この戦略的な軸足は、国の宇宙政策に沿うだけでなく、国際的なサプライヤーへの依存を減らすことで運用の安定性を高める。国内調達は、より良いコスト管理をサポートし、納期を改善し、安全規制への準拠をより確実にします。
2024年には、中型ロケットが56.63%のシェアで市場を席巻します。これらのロケットは、ペイロード容量と運用効率の理想的な組み合わせを提供し、幅広い打上げミッションに人気のある選択肢となっています。その柔軟性により、単一顧客のペイロードとライドシェアミッションの両方に対応できるため、民間事業者や政府機関にとっても非常に魅力的です。地球低軌道(LEO)と静止トランスファー軌道(GTO)の両方に到達する能力を持つ中型リフト機は、依然として打上げ業界の主力です。
低軌道は軌道タイプ別でリードを維持し、2024年には市場の53.49%を占める。低軌道の人気は、低遅延、データ伝送の高速化、配備コストの削減といった利点に起因します。これらの要素は、ブロードバンド接続、監視、環境モニタリングなどの用途に不可欠です。LEOは地球に近いため、スケーラブルでコスト効率の高い方法で高密度の衛星コンステレーションを展開できます。低遅延通信サービスやリアルタイムデータソリューションの提供を目指す企業は、LEOをますますターゲットにするようになっており、商業宇宙活動の戦略的ホットスポットとなっています。
米国の商業宇宙打上げ市場は、強力な官民協力に支えられ、2034年までに124億米ドルに達すると予測されます。規制の合理化、技術革新のインセンティブ、インフラへの投資が、米国を世界の宇宙リーダーとして前進させています。公的資金、民間企業とのパートナーシップ、研究開発イニシアティブは、再使用可能な打上げシステムやモジュール式衛星ペイロードの画期的な進歩を早めています。宇宙機関は、次世代の打上げ能力を向上させるために、民間企業と手を携えて努力を続けています。
世界市場を形成する主な企業には、SpaceX、United Launch Alliance、Rocket Lab USA、Blue Origin、Safran S.A.などがいます。これらの企業は、ミッションコストの削減と打上げ頻度の増加を目指し、再使用可能な打上げシステムを積極的に開発しています。防衛機関や通信プロバイダーとの戦略的提携により、長期契約の確保が可能になっています。民間打上げインフラに投資し、製造プロセスを垂直統合し、世界なパートナーシップを結ぶことで、これらの企業はサプライチェーンの強靭性を強化し、運用の柔軟性を高め、国際的なリーチを広げています。
目次
第1章 調査手法と範囲
第2章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第3章 業界考察
- エコシステム分析
- トランプ政権による関税への影響
- 貿易への影響
- 貿易量の混乱
- 報復措置
- 業界への影響
- 供給側の影響(サービスプロバイダー)
- 主要サービスの価格変動
- サプライチェーンの再構築
- 生産コストへの影響
- 需要側の影響(価格設定)
- 最終市場への価格伝達
- 市場シェアの動向
- 消費者の反応パターン
- 供給側の影響(サービスプロバイダー)
- 影響を受ける主要企業
- 戦略的な業界対応
- サーバープロバイダーの再構成
- 価格設定とサービス戦略
- 政策関与
- 展望と今後の検討事項
- 貿易への影響
- 業界への影響要因
- 促進要因
- 小型衛星打ち上げ需要の増加
- 再使用型打ち上げロケットへの注目の高まり
- 民間の打ち上げ業者と宇宙港の出現
- 官民連携の強化
- 宇宙観光と弾道飛行の拡大
- 業界の潜在的リスク&課題
- 高い立ち上げコストと資本集約度
- 規制と安全コンプライアンスの複雑さ
- 促進要因
- 成長可能性分析
- 規制情勢
- テクノロジーの情勢
- 将来の市場動向
- ギャップ分析
- ポーター分析
- PESTEL分析
第4章 競合情勢
- イントロダクション
- 企業の市場シェア分析
- 主要市場企業の競合分析
- 競合ポジショニングマトリックス
- 戦略ダッシュボード
第5章 市場推計・予測:ペイロードタイプ別、2021-2034
- 主要動向
- 衛星
- 貨物・物流
- 有人宇宙飛行
- 惑星間ミッション
第6章 市場推計・予測:ロケットの種類別、2021-2034
- 主要動向
- 小型ロケット(2,000 kg未満)
- 中型ロケット(2,000~20,000 kg)
- 大型打ち上げロケット(20,000 kg以上)
第7章 市場推計・予測:軌道タイプ別、2021-2034
- 主要動向
- 低地球軌道(LEO)
- 静止軌道(GEO)
- 中軌道(MEO)
- 極軌道および太陽同期軌道(SSO)
- 深宇宙
第8章 市場推計・予測:最終用途別、2021-2034
- 民間衛星事業者
- 政府と民間のパートナーシップ
- 宇宙観光企業
- 調査・学術機関
- 防衛と軍事
第9章 市場推計・予測:地域別、2021 –2034
- 主要動向
- 北米
- 米国
- カナダ
- 欧州
- ドイツ
- 英国
- フランス
- スペイン
- イタリア
- アジア太平洋地域
- 中国
- インド
- 日本
- オーストラリア・ニュージーランド
- 韓国
- ラテンアメリカ
- ブラジル
- メキシコ
- 中東・アフリカ
- アラブ首長国連邦
- サウジアラビア
- 南アフリカ
第10章 企業プロファイル
- Agnikul Cosmos
- Astra
- Blue Origin
- Firefly Aerospace
- GALACTIC ENERGY
- Isar Aerospace SE
- ispace
- LandSpace
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries、Ltd.
- Northrop Grumman
- PLD Space
- Relativity Space
- Rocket Lab USA
- Safran S.A.
- SpaceX
- United Launch Alliance、LLC.
- Skyroot Aerospace
The Global Commercial Space Launch Market was valued at USD 8.2 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 14.6% to reach USD 31.9 billion by 2034. This explosive growth is fueled by rapid advancements in space technologies, increasing affordability of launch services, and rising demand for connectivity, Earth observation, and scientific research. The global space economy is undergoing a fundamental shift as commercial players become more active and influential, transforming what was once a government-dominated sector into a competitive, innovation-driven industry. Miniaturization of satellites and reduced manufacturing costs have made it easier for private and institutional customers to access space.

With growing interest in low Earth orbit satellite constellations, weather monitoring, real-time imaging, and next-generation communications, the commercial space launch sector has evolved into a key pillar of the broader aerospace ecosystem. As the space economy diversifies beyond traditional exploration, opportunities in data services, inter-satellite links, and space-based infrastructure continue to open new frontiers. Countries around the world are investing heavily in launch infrastructure, regulatory reform, and research and development, making the commercial space launch market a magnet for both capital and talent.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2025-2034 |
| Start Value | $8.2 Billion |
| Forecast Value | $31.9 Billion |
| CAGR | 14.6% |
Demand for small satellite launches has skyrocketed due to the rising feasibility of deploying compact payloads that serve a wide range of functions across communication, Earth imaging, climate tracking, and scientific experimentation. The ability to launch smaller satellites more frequently and affordably is a game-changer for both commercial enterprises and government agencies. This transformation has been accelerated by significant reductions in launch costs and the introduction of cost-effective miniaturization technologies.
As a result, companies now have greater access to orbital platforms, enabling the rapid deployment of innovative satellite services. Increased participation from the private sector in launch operations, combined with supportive government policies and streamlined licensing procedures, is reshaping the global space launch ecosystem. A growing number of dedicated launch sites and regional spaceports are being developed to support the increasing volume and variety of commercial missions. This expansion is drawing in a broader base of institutional and commercial clients, contributing to a sharp increase in launch frequency.
However, geopolitical trade tensions and fluctuating international policies have added complexity to the industry's cost structure. Import tariffs on aerospace components and propulsion systems have disrupted supply chains and increased production costs. To mitigate these risks, companies are moving toward localizing production and sourcing materials domestically. This strategic pivot not only aligns with national space policies but also enhances operational stability by reducing reliance on international suppliers. Domestic sourcing supports better cost control, improves delivery timelines, and ensures greater compliance with security regulations.
In 2024, medium-lift launch vehicles dominated the market with a 56.63% share. These rockets offer the ideal combination of payload capacity and operational efficiency, making them a popular choice for a broad spectrum of launch missions. Their flexibility allows them to accommodate both single-customer payloads and ride-share missions, which is highly attractive to commercial operators and government agencies alike. With capabilities to reach both low Earth orbit (LEO) and geostationary transfer orbit (GTO), medium-lift vehicles remain the workhorses of the launch industry.
Low Earth orbit maintained the lead by orbit type, capturing 53.49% of the market in 2024. Its popularity stems from advantages such as low latency, faster data transmission, and reduced deployment costs. These factors are critical for applications like broadband connectivity, surveillance, and environmental monitoring. LEO's proximity to Earth allows for the deployment of dense satellite constellations in a scalable, cost-efficient manner. Companies aiming to deliver low-latency communication services and real-time data solutions are increasingly targeting LEO, making it a strategic hotspot for commercial space activity.
The United States Commercial Space Launch Market is forecasted to reach USD 12.4 billion by 2034, underpinned by strong public-private collaboration. Streamlined regulations, innovation incentives, and investments in infrastructure are driving the U.S. forward as a global space leader. Public funding, partnerships with private firms, and R&D initiatives are fast-tracking breakthroughs in reusable launch systems and modular satellite payloads. Agencies continue to work hand-in-hand with commercial players to advance next-generation launch capabilities.
Key players shaping the global market landscape include SpaceX, United Launch Alliance, Rocket Lab USA, Blue Origin, and Safran S.A. These companies are actively developing reusable launch systems to lower mission costs and increase launch frequency. Strategic collaborations with defense organizations and telecom providers are enabling them to secure long-term contracts. By investing in private launch infrastructure, vertically integrating manufacturing processes, and entering global partnerships, these firms are strengthening supply chain resilience, increasing operational flexibility, and extending their international reach.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Methodology and Scope
- 1.1 Market scope and definitions
- 1.2 Research design
- 1.2.1 Research approach
- 1.2.2 Data collection methods
- 1.3 Base estimates and calculations
- 1.3.1 Base year calculation
- 1.3.2 Key trends for market estimation
- 1.4 Forecast model
- 1.5 Primary research and validation
- 1.5.1 Primary sources
- 1.5.2 Data mining sources
Chapter 2 Executive Summary
- 2.1 Industry 360° synopsis
Chapter 3 Industry Insights
- 3.1 Industry ecosystem analysis
- 3.2 Trump administration tariffs
- 3.2.1 Impact on trade
- 3.2.1.1 Trade volume disruptions
- 3.2.1.2 Retaliatory measures
- 3.2.2 Impact on the industry
- 3.2.2.1 Supply-side impact (service providers)
- 3.2.2.1.1 Price volatility in key services
- 3.2.2.1.2 Supply chain restructuring
- 3.2.2.1.3 Production cost implications
- 3.2.2.2 Demand-side impact (pricing)
- 3.2.2.2.1 Price transmission to end markets
- 3.2.2.2.2 Market share dynamics
- 3.2.2.2.3 Consumer response patterns
- 3.2.2.1 Supply-side impact (service providers)
- 3.2.3 Key companies impacted
- 3.2.4 Strategic industry responses
- 3.2.4.1 Server provider reconfiguration
- 3.2.4.2 Pricing and service strategies
- 3.2.4.3 Policy engagement
- 3.2.5 Outlook and future considerations
- 3.2.1 Impact on trade
- 3.3 Industry impact forces
- 3.3.1 Growth drivers
- 3.3.1.1 Growth in small satellite launch demand
- 3.3.1.2 Rising focus on reusable launch vehicles
- 3.3.1.3 Emergence of private launch providers and spaceports
- 3.3.1.4 Increased government-private sector collaborations
- 3.3.1.5 Expansion of space tourism and suborbital flights
- 3.3.2 Industry pitfalls and challenges
- 3.3.2.1 High launch costs and capital intensity
- 3.3.2.2 Regulatory and safety compliance complexities
- 3.3.1 Growth drivers
- 3.4 Growth potential analysis
- 3.5 Regulatory landscape
- 3.6 Technology landscape
- 3.7 Future market trends
- 3.8 Gap analysis
- 3.9 Porter's analysis
- 3.10 PESTEL analysis
Chapter 4 Competitive Landscape, 2024
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Company market share analysis
- 4.3 Competitive analysis of major market players
- 4.4 Competitive positioning matrix
- 4.5 Strategy dashboard
Chapter 5 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Payload Type, 2021-2034 (USD Billion)
- 5.1 Key trends
- 5.2 Satellites
- 5.3 Cargo & logistics
- 5.4 Human spaceflight
- 5.5 Interplanetary missions
Chapter 6 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Launch Vehicle Type, 2021-2034 (USD Billion)
- 6.1 Key trends
- 6.2 Small-lift launch vehicles (< 2,000 kg)
- 6.3 Medium-lift launch vehicles (2,000–20,000 kg)
- 6.4 Heavy-lift launch vehicles (> 20,000 kg)
Chapter 7 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Orbit Type, 2021-2034 (USD Billion)
- 7.1 Key trends
- 7.2 Low earth orbit (LEO)
- 7.3 Geostationary orbit (GEO)
- 7.4 Medium earth orbit (MEO)
- 7.5 Polar & sun-synchronous orbit (SSO)
- 7.6 Deep space
Chapter 8 Market Estimates & Forecast, By End Use, 2021-2034 (USD Billion)
- 8.1 Private satellite operators
- 8.2 Government-commercial partnerships
- 8.3 Space tourism companies
- 8.4 Research & academic institutions
- 8.5 Defense & military
Chapter 9 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Region, 2021 – 2034 (USD Billion)
- 9.1 Key trends
- 9.2 North America
- 9.2.1 U.S.
- 9.2.2 Canada
- 9.3 Europe
- 9.3.1 Germany
- 9.3.2 UK
- 9.3.3 France
- 9.3.4 Spain
- 9.3.5 Italy
- 9.4 Asia Pacific
- 9.4.1 China
- 9.4.2 India
- 9.4.3 Japan
- 9.4.4 ANZ
- 9.4.5 South Korea
- 9.5 Latin America
- 9.5.1 Brazil
- 9.5.2 Mexico
- 9.6 Middle East and Africa
- 9.6.1 UAE
- 9.6.2 Saudi Arabia
- 9.6.3 South Africa
Chapter 10 Company Profiles
- 10.1 Agnikul Cosmos
- 10.2 Astra
- 10.3 Blue Origin
- 10.4 Firefly Aerospace
- 10.5 GALACTIC ENERGY
- 10.6 Isar Aerospace SE
- 10.7 ispace
- 10.8 LandSpace
- 10.9 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- 10.10 Northrop Grumman
- 10.11 PLD Space
- 10.12 Relativity Space
- 10.13 Rocket Lab USA
- 10.14 Safran S.A.
- 10.15 SpaceX
- 10.16 United Launch Alliance, LLC.
- 10.17 Skyroot Aerospace


