|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1489500
エタノールの世界市場-2024-2031Global Ethanol Market - 2024-2031 |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| エタノールの世界市場-2024-2031 |
|
出版日: 2024年06月05日
発行: DataM Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 213 Pages
納期: 即日から翌営業日
|
- 全表示
- 概要
- 目次
概要
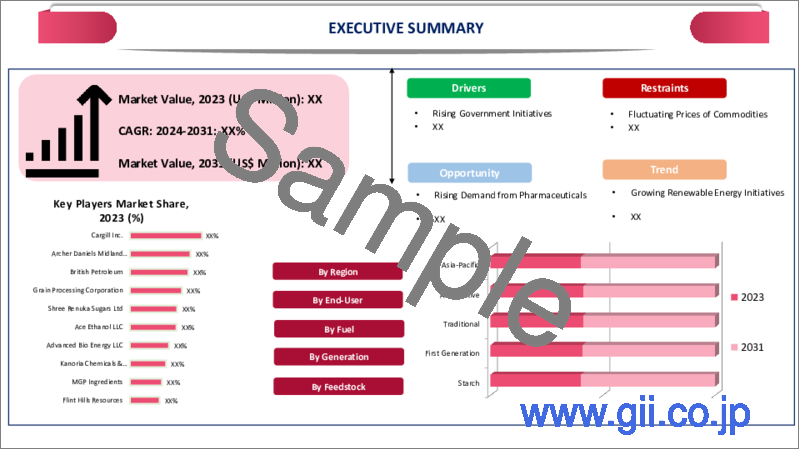
世界のエタノール市場は、2023年に1,025億米ドルに達し、2024年から2031年の予測期間中にCAGR 5.2%で成長し、2031年には1,538億米ドルに達すると予測されています。北米、特に米国は世界のエタノール需要を牽引しています。近年の力強い経済成長により、北米は急速に金融、貿易、産業の世界の中心地となっています。
エタノールは、植物原料や農業製品別などの天然資源から抽出することができます。これらの資源からエタノールを製造するプロセスは、他のエネルギー源に比べてエネルギー集約的でないため、長期的に持続可能な選択肢となります。さらに、エタノールは化石燃料よりも二酸化炭素排出量が少ないため、燃やしたときに大気中に有害な排出物をあまり排出せず、環境に優しい選択肢となっています。
エタノールは直接液体燃料に変換することができるため、このように人気の高い選択肢となり、輸送用エネルギー需要を満たすために使用されるようになった。エタノール産業やその他のバイオ燃料産業は急速に普及しており、このような要因からエタノール市場は継続的に成長しています。
さらに、エタノールから汚染物質を除去・低減するために高度なろ過方法が使用されるようになり、その結果、限外ろ過やナノろ過などの新しいろ過システムの設置が進み、より高品質の製品が得られるようになった。UFおよびNFシステムは、異なるサイズの分子を分離するために異なる膜材料を使用しており、エタノールをより徹底的に精製することができます。
世界のエタノール市場は、輸送部門からの需要増加により、近年一定の成長を見せています。運輸部門で特に伸びているのは、従来のガソリンやディーゼル燃料に比べて燃焼効率が高く、二酸化炭素排出量が少ないためです。また、他の燃料に比べて一般的に安価であるため、消費者の価格節約につながる可能性があることも利点のひとつです。
さらに、微生物燃料電池は、トウモロコシの茎、サトウキビのバガス、醸造廃水などの農業廃棄物や廃水から再生可能エネルギーを生産するのに使用できるため、石油・ガスなどの伝統的な燃料源に代わる魅力的な選択肢となり、この分野で大きな発展を遂げています。
ダイナミクス
再生可能ガソリンとしてのエタノールの利点
エタノールは、再生可能ガソリンの信頼できる供給源として、現代社会で人気が高まっています。その再生可能でクリーンな燃焼特性、および環境におけるその豊富さが、市場での人気の主な理由です。エタノールを再生可能ガソリンの原料として使用する主な利点は、その再生可能な性質とそれがもたらす環境への好影響に関連しています。最も顕著な利点は、エタノールが再生可能な資源であるため、有限な化石燃料への依存を減らすことができることです。
エタノールが再生可能燃料の選択肢として人気を集めているのは、その環境面での利点による。エタノールは、従来のガソリンよりも炭素や窒素酸化物の排出量が少なく、よりクリーンな燃焼が可能です。再生可能な原料は持続可能で、石油ベースの燃料よりも環境への影響が少ないです。そのため、多くの業界が再生可能燃料としてのエタノールの利用を促進する取り組みを実施しています。
また、米国エネルギー省が高度バイオ燃料を生産する商業規模のバイオリファイナリーの開発、建設、改修を支援するために創設した融資保証プログラムなど、バイオ燃料生産を促進するための政府補助金やイニシアチブも数多く存在します。
クリーンな燃料への需要の高まり
再生可能なバイオ燃料としてのエタノールが台頭し、人気を博していることは、自動車産業の主要部分であることを証明しています。燃費の向上と排出ガスの削減に対する需要が絶えず高まっているため、より効率的でクリーンな燃焼燃料源に対する消費者の需要が高まっています。その結果、エタノールと再生可能バイオ燃料の市場は過去数年間で劇的に成長しました。エタノールは、手頃な価格でクリーンな燃焼が可能な燃料として、消費者の人気を集めています。
環境に優しい燃料源に対する需要が高まっている背景には、従来型燃料のコスト上昇、排出ガスに関する環境問題、再生可能エネルギー源の使用に対する政府や州の優遇措置など、いくつかの要因があります。ブラジルでは、政府が石油系燃料を使用する際の税金を、エタノール系燃料を使用する場合よりも引き上げています。このため、エタノールガソリンの需要が大幅に増加し、エタノール市場の成長を後押ししています。
エタノール・バイオ燃料で環境に優しい未来を築く
エタノール・バイオ燃料は、温室効果ガスの排出を削減する可能性があるため、環境に優しいエネルギー源として古くから利用されてきました。エタノール・バイオ燃料は、化石燃料とは異なり、燃焼時に二酸化炭素を放出しないため、温室効果ガスの排出を削減する可能性があります。その結果、エタノール・バイオ燃料の生産と使用により、温室効果ガスの排出を最大88%削減できると推定されています。
エタノール・バイオ燃料は化石燃料よりもきれいに燃焼するため、大気汚染に関しても環境に優しい選択肢となります。大気汚染の主な原因である揮発性有機化合物、粒子状物質、窒素酸化物の排出量は、エタノール・バイオ燃料の方が大幅に少ないです。
従来のガスに代わる安価な燃料
エタノール燃料は通常、従来のガソリンよりも安く、その価格差は地域によってはかなり大きなものになります。エタノール燃料の生産コストが低いのは、石油や石炭のような有限資源を必要としない再生可能な性質によるところが大きく、またコスト削減はエタノール・バイオ燃料の最も大きなメリットです。
エタノール・バイオ燃料は、再生可能エネルギー分野での雇用創出に貢献します。エタノール燃料の生産に投資することで、企業は再生可能エネルギーに関心のある個人の雇用機会を増やすことができます。しかし、再生可能エネルギー関連の仕事が増え、その仕事に適任な人に与えられることで、経済の活性化にもつながります。
限られたエタノール生産
エタノールの供給が制限されているため、いくつかの国では需給に混乱が生じ、エタノールの価格が上昇したり供給が不足したりして、世界のエタノール市場に大きな影響を与えています。また、供給が制限されているため、粗悪なエタノールや低品質のエタノールが生産されるリスクが高まっており、市場全体の評判に影響を与える可能性があります。
米国農務省(USDA)によると、世界のエタノール生産量は2018年の約950億リットルから2022年には850億リットルに減少しており、これは主に中国やインドなど特定の国におけるエタノールの入手可能性の低下とCOVID-19の悪影響によるものです。エタノールの利用可能量の減少は、バイオディーゼルや再生可能ディーゼルのような他のバイオ燃料に対する需要の増加と、トウモロコシやサトウキビのような原料の利用可能量の減少によるものです。
エタノール・バイオ燃料規制の課題
エタノール・バイオ燃料の生産と使用に関する政府の政策やインセンティブは、警告なしに素早く変更される可能性があり、この不確実性が、エタノール・バイオ燃料への投資によるビジネスの増減につながっています。規制の不確実性は、エタノール・バイオ燃料の生産と使用に投資する企業にとって、予測が難しく、またナビゲートも難しい問題です。
米国環境保護庁は、連邦再生可能燃料基準を定め、燃料精製業者に毎年一定割合のエタノールをガソリンに添加することを義務付けています。再生可能燃料基準値が低く設定されすぎると、エタノールの需要が減少し、価格が下がり、エタノール生産者の収益性が低下する可能性があります。
目次
第1章 調査手法と調査範囲
第2章 定義と概要
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場力学
- 影響要因
- 促進要因
- 再生可能ガソリンとしてのエタノールの利点
- クリーンな燃料への需要の高まり
- エタノール・バイオ燃料で環境に優しい未来を作る
- 従来のガスに代わる安価な燃料
- 抑制要因
- エタノールの生産量に限界がある
- エタノール・バイオ燃料規制の課題
- 機会
- 影響分析
- 促進要因
第5章 産業分析
- ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- サプライチェーン分析
- 価格分析
- 規制分析
- ロシア・ウクライナ戦争影響分析
- DMIの見解
第6章 COVID-19分析
第7章 原料別
- 澱粉
- 穀物
- トウモロコシ
- 大麦
- ライ麦
- 小麦
- ソルガム穀物
- 根菜類
- ジャガイモ
- キャッサバ
- 穀物
- 砂糖
- テンサイ
- サトウキビ
- スイートソルガム
- セルロース原料
- 農作物残渣
- わら
- トウモロコシ茎葉
- バガス
- 木材/森林残渣
- エネルギー専用作物
- 柳
- ポプラ
- スイッチグラス
- 産業廃棄物およびその他の廃棄物
- 農作物残渣
第8章 世代別
- 第一世代
- 第二世代
- 第三世代
第9章 燃料タイプ別
- 従来型
- バイオエタノール
- E5
- E10
- E15~E70
- E75~E85
- その他
第10章 エンドユーザー別
- 自動車
- 飲食品
- 医薬品
- 化粧品
- 燃料電池
- 肥料
- 殺虫剤
- 工業用溶剤
- その他
第11章 地域別
- 北米
- 米国
- カナダ
- メキシコ
- 欧州
- ドイツ
- 英国
- フランス
- イタリア
- ロシア
- その他欧州
- 南米
- ブラジル
- アルゼンチン
- その他南米
- アジア太平洋
- 中国
- インド
- 日本
- オーストラリア
- その他アジア太平洋地域
- 中東・アフリカ
第12章 競合情勢
- 競合シナリオ
- 市況/シェア分析
- M&A分析
第13章 企業プロファイル
- ADM
- 会社概要
- 製品ポートフォリオと説明
- 財務概要
- 主な発展
- Cargill, Incorporated
- Solvay
- Mitsubishi Chemical Company
- Heineken
- AB Miller
- British Petroleum
- The Andersons Inc.
- Advanced Bioenergy LLC
- Stake Technology
第14章 付録
Overview
Global Ethanol Market reached US$ 102.5 Billion in 2023 and is expected to reach US$ 153.8 Billion by 2031 growing with a CAGR of 5.2% during the forecast period 2024-2031. North America and particularly United States, is a major driver of global demand for ethanol. With their strong economic growth in recent years, they have quickly become the world's leading hub for finance, trade and industry.
Ethanol can be extracted from natural sources like plant material and agricultural by-products. The process of creating ethanol from these resources is much less energy-intensive than other sources of energy, making it a much more sustainable option over the long-term. In addition, ethanol has a much lower carbon footprint than fossil fuels which means that it does not produce as many harmful emissions into the atmosphere when it is burned, making it an environmentally friendly choice.
Ethanol became such a popular choice due to its ability to be directly converted into liquid fuels, which can then be used to meet transportation energy needs, the ethanol industry and other biofuel industries are quickly becoming more and more popular and because of this factor the ethanol market is on continuous growth.
Furthermore, advanced filtration methods are now being used to remove and reduce contaminants from ethanol, resulting in a higher quality product which further includes the installation of new filtration systems, such as ultrafiltration and nanofiltration .UF and NF systems use different membrane materials to separate molecules of different sizes, allowing for a more thorough purification of the ethanol.
The global ethanol market has seen constant growth in recent years due to the increased demand from the transportation sector. Particular growth in the transportation sector is due to its efficient combustion and low carbon emissions relative to traditional gasoline and diesel fuels. Another advantage includes potential price savings to consumers because it is typically cheaper than other fuels.
Furthermore, microbial fuel cells are the major development in this sector which is having several benefits as they can be used to produce renewable energy from agricultural waste and wastewater, such as corn stalks, sugarcane bagasse and brewery wastewater, that makes them an attractive alternative to traditional fuel sources such as oil and gas.
Dynamics
Benefits Of Ethanol As Renewable Gasoline
Ethanol is becoming increasingly popular as a reliable source of renewable gasoline in the modern world. Its renewable and clean burning properties, as well as its abundance in the environment are the major reasons for its popularity in the market. The main advantages of using ethanol as a source of renewable gasoline are related to its renewable nature and the positive environmental impacts it can have. The most prominent benefit is that ethanol is a renewable resource, so it can reduce our dependence on finite fossil fuel.
Ethanol is gaining popularity as a renewable fuel option due to its environmental benefits. It produces fewer carbon and nitrogen oxide emissions than traditional gasoline, making it a cleaner burning alternative. Its renewable source materials are sustainable and have a lesser environmental impact than petroleum-based fuels. So many industries have implemented initiatives to promote the use of ethanol as a renewable fuel source.
Also, So many government subsidies and initiatives are there to promote the biofuel production such as the loan guarantee program created by U.S. Department of Energy to help fund the development, construction and retrofitting of commercial-scale biorefineries that produce advanced biofuels.
Growing Demand For A Clean Burning Fuel
Ethanol as a renewable biofuel market is emerging and gaining popularity which proves it as a major part of the automotive industry. The constant increasing demand for better fuel efficiency and reduced emissions has led to an increasing demand from consumers for more efficient and clean burning fuel sources. As a result, the market for ethanol and renewable biofuels has grown dramatically in past years. Ethanol, in, is becoming more popular with consumers as an affordable and clean burning fuel option.
The demand for environmentally friendly fuel sources is increasing because of several factors, including the rising cost of conventional fuels, environmental concerns about emissions and governmental and state incentives for the use of renewable energy sources. In Brazil, the government increased tax prices on using petroleum-based fuels than it does for using ethanol-based fuels. Because of this a significant increase in the demand for ethanol-based gasoline is being reflected and helped to fuel a growth in the ethanol market.
Crafting a Greener Future with Ethanol Biofuel
Ethanol biofuel has been used from long time as an environmentally friendly source of energy due to its potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions Ethanol biofuel has the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions because it does not release carbon dioxide as it burns, unlike fossil fuels. As a result, production and use of ethanol biofuel is estimated to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 88%.
Ethanol biofuel burns cleaner than fossil fuels, making it a more environmentally friendly option when it comes to air pollution. The emissions generated by ethanol biofuel are significantly lower in terms of volatile organic compounds, particulate matter and nitrogen oxides, which are some of the primary causes of air pollution.
An Inexpensive Alternative to Traditional Gas
Ethanol fuel is typically cheaper than traditional gasoline and that price difference can be quite substantial depending on the region. The lower cost of production for ethanol fuel is largely due to its renewable nature, which does not require finite resources like oil and coal, also the reduce cost is the most significant benefits of ethanol biofuel.
Ethanol biofuel can help create jobs in the renewable energy sector. By investing in the production of ethanol fuel, businesses can create more job opportunities for individuals who are interested in renewable energy. However, this can also help to stimulate the economy, as more renewable energy-related jobs are created and given to those who are qualified for them.
Limited Production Of Ethanol
The limited availability of ethanol is having a significant impact on the global ethanol market in several countries, as it has created a disruption in supply and demand which has resulted in higher prices for ethanol and a lack of supply in some countries. Also, due to the limited availability, there is an increased risk of adulterated ethanol and lower quality ethanol being produced, which can impact the overall market's reputation.
According to U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) global ethanol production decreased from nearly 95 billion liters in 2018 to 85 billion liters in 2022,which was primarily due to reduced availability of ethanol in certain countries, such as China and India and the negative impact of COVID-19. Reduction in ethanol availability is due to an increased demand for other biofuels, like biodiesel and renewable diesel, as well as a decrease in the availability of feedstocks, like corn and sugarcane.
Challenges of Ethanol Biofuel Regulation
Government policies and incentives for the production and use of ethanol biofuel can change quickly and without warning and this uncertainty leads to up and down in businesses from investing in the fuel. Regulatory uncertainty is an issue that is difficult to predict and also difficult to navigate for businesses invested in the production and use of ethanol biofuel.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency has set the federal renewable fuel standard that requires fuel refiners to provide a certain percentage of ethanol into their gasoline each year. When the renewable fuel standard levels are set too low, the demand for ethanol can decrease, leading to lower prices and reduced profitability for ethanol producers.
Segment Analysis
The global ethanol market is segmented based on potential of feedstock, generation, fuel type, end-user and region.
Starch-based Feedstocks an important source
Starch-based feedstock is an important source of energy in many industries, primarily for producing ethanol. It is derived from a variety of crops, most commonly corn, but also potatoes, sweet potatoes, tapioca, rice, rye and barley. Corn is the most common source of starch-based feedstock due to its high production in agriculture all globally and cost-effectiveness, as well as the fact that it provides a high yield of ethanol. Due to this reason, it is the preferred option for many energy companies
Potatoes are another source of starch-based feedstock and offer a number of advantages compared to corn. Potatoes contain more starch than corn, which results in more ethanol being produced. Furthermore, potatoes are a more sustainable option as they require less area land and water to grow. Sweet potatoes, tapioca, rice, rye and barley are also used as sources of starch-based feedstock, but to a lesser extent than corn and potatoes.
Geographical Penetration
North-America is Growing owing to government initiatives
North America globally accounts for a large production of Ethanol. According to a report from the Renewable Fuels Association, U.S. is the leading producer and consumer of ethanol globally. The US is also the world's largest market for ethanol, accounting for nearly 1/3 of global ethanol consumption. Within U.S., the majority of ethanol in the fuel supply comes from corn ethanol. In the Automotive and biofuel segment, the trend has been similar, with US being the top producer and consumer of ethanol-based fuel.
The US ethanol industry has benefited from government incentives and supportive policies, as well as from an increase in the number of cars capable of using ethanol-blended gasoline. The US is well-positioned to remain the world's leading ethanol producer, given its vast supply of corn and other feedstock, advanced Feedstock Biofuel and supportive policies. Going forward, US will continue to be a major player in the global ethanol market.
Competitive Landscape
The major global players in the market include Royal Dutch Shell, BP, Valero Energy Corporation, Petrobras, Chevron Corporation, Sasol, Cenovus Energy Inc., PBF Energy, Husky Energy, Abengoa Bioenergy
COVID-19 Impact Analysis
The impact of COVID-19 on the global ethanol market has been significant. The coronavirus pandemic has led to a reduction in global demand for crude oil as transportation restrictions and lockdowns have led to a reduction in overall mobility which in turn, has led to a decline in demand for gasoline fuel, creating an opportunity for ethanol to replace gasoline as an automotive fuel.
Global ethanol production has increased significantly since the pandemic began in 2020. The increment is primarily due to the increased demand for ethanol as a gasoline fuel substitute. The increased demand for ethanol as a fuel substitute has also led to a surge in prices. Also increase in price has led to a more profitable ethanol industry, which has attracted additional investment from the private sector.
Russia-Ukraine War Analysis
Russia and Ukraine's ongoing conflict has had an impact on global ethanol production markets. While the conflict has yet to directly affect ethanol production, it has caused instability in global markets. Ethanol prices have been volatile after the conflict due to increased uncertainty and reduced trading activity which has resulted in a decrease in investments in the region, which has in turn affected ethanol production.
The war impact caused a decrease in Ukrainian production of ethanol and gasoline which led to a decrease in global production, as Ukraine was one of the major players in the global ethanol and gasoline markets prior to the conflict. Also decrease in production of ethanol and gasoline due to Ukraine-Russia conflict caused a notable impact on global supply and demand.
By Feedstock
- Starch
- Cereals
- Corn
- Barley
- Rye
- Wheat
- Sorghum Grain
- Root Crops
- Potato
- Cassava
- Sugars
- Sugar Beets
- Sugar Cane
- Sweet Sorghum
- Cellulosic Materials
- Crop Residues
- Straw
- Corn Stover
- Bagasse
- Wood/Forest Residues
- Dedicated Energy Crops
- Willow
- Poplar
- Switchgrass
- Industrial and Other Wastes
By Generation
- First Generation
- Second Generation
- Third Generation
By Fuel Type
- Traditional
- Bioethanol
- E5
- E10
- E15 to E70
- E75 to E85
- Others
By End-User
- Automotive
- Food and Beverage
- Pharmaceuticals
- Cosmetics
- Fuel Cells
- Fertilizers
- Pesticides
- Industrial Solvent
- Others
By Region
- North America
- U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Germany
- UK
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of South America
- Asia-Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- Australia
- Rest of Asia-Pacific
- Middle East and Africa
Key Development
- In June 2023, the Renewable Fuels Association (RFA) Governor Cooper said that under the Feedstock-neutral carbon-reduction program, which features ethanol and other renewable liquid fuels as key components. Governor Cooper confidently proclaimed that corn ethanol today has a carbon footprint that is already 50 percent smaller than gasoline and that RFA members have made a commitment to reach net zero emissions from ethanol by the year 2050 and even sooner. Governor Cooper also highlighted the fact that ethanol is a low-cost and low-carbon solution that is readily available today to help propel the global energy transition.
- On March 25, 2023, RFA the Renewable Fuel Association announced a summer contest with a prize of free fuel. The contest, which is slated to launch in 2023, will offer contestants the chance to win up to two years of free fuel which is an incredible opportunity, both for the winners and for the environment. As the Energy Transition becomes more pressing, this contest provides an incentive for people to make the switch to renewable fuel sources, mainly Ethanol.
- In June 2023, Bharat Petroleum is launching a revolutionary initiative to help revolutionize sustainable transportation. Through its Ethanol Blended Diesel (EBD) and Flex Fuel Program, the oil major is introducing an extensive range of alternative fuels to reduce emissions from diesel-run vehicles. The program will help reduce the dependency of diesel-run vehicles on traditional fuels and will also promote the use of cleaner fuels.
Why Purchase the Report?
- To visualize the global ethanol market segmentation based on the feedstock, generation, fuel type, end-user and region, as well as understand key commercial assets and players.
- Identify commercial opportunities by analyzing trends and co-Development.
- Excel data sheet with numerous data points of ethanol market-level with all segments.
- The PDF report consists of a comprehensive analysis after exhaustive qualitative interviews and an in-depth study.
- Product mapping available as Excel consisting of key products of all the major players.
The Global Ethanol Market report would provide approximately 68 tables, 70 figures and 213 Pages.
Target Audience 2024
- Government policy makers
- Alcohol manufacturers
- Renewable fuel producers
- Automotive manufacturers
Table of Contents
1.Methodology and Scope
- 1.1.Research Methodology
- 1.2.Research Objective and Scope of the Report
2.Definition and Overview
3.Executive Summary
- 3.1.Snippet by Feedstock
- 3.2.Snippet by Generation
- 3.3.Snippet by Fuel Type
- 3.4.Snippet by End-User
- 3.5.Snippet by Region
4.Dynamics
- 4.1.Impacting Factors
- 4.1.1.Drivers
- 4.1.1.1.Benefits Of Ethanol As Renewable Gasoline
- 4.1.1.2.Growing Demand For A Clean Burning Fuel
- 4.1.1.3.Crafting a Greener Future with Ethanol Biofuel
- 4.1.1.4.An Inexpensive Alternative to Traditional Gas
- 4.1.2.Restraints
- 4.1.2.1.Limited Production Of Ethanol
- 4.1.2.2.Challenges of Ethanol Biofuel Regulation
- 4.1.3.Opportunity
- 4.1.4.Impact Analysis
- 4.1.1.Drivers
5.Industry Analysis
- 5.1.Porter's Five Force Analysis
- 5.2.Supply Chain Analysis
- 5.3.Pricing Analysis
- 5.4.Regulatory Analysis
- 5.5.Russia-Ukraine War Impact Analysis
- 5.6.DMI Opinion
6.COVID-19 Analysis
- 6.1.Analysis of COVID-19
- 6.1.1.Scenario Before COVID-19
- 6.1.2.Scenario During COVID-19
- 6.1.3.Scenario Post COVID-19
- 6.2.Pricing Dynamics Amid COVID-19
- 6.3.Demand-Supply Spectrum
- 6.4.Government Initiatives Related to the Market During Pandemic
- 6.5.Manufacturers Strategic Initiatives
- 6.6.Conclusion
7.By Feedstock
- 7.1.Introduction
- 7.1.1.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Feedstock
- 7.1.2.Market Attractiveness Index, By Feedstock
- 7.2.Starch*
- 7.2.1.Introduction
- 7.2.2.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%)
- 7.2.3.Cereals
- 7.2.3.1.Corn
- 7.2.3.2.Barley
- 7.2.3.3.Rye
- 7.2.3.4.Wheat
- 7.2.3.5.Sorghum Grain
- 7.2.4.Root Crops
- 7.2.4.1.Potato
- 7.2.4.2.Cassava
- 7.3.Sugars
- 7.3.1.Sugar Beets
- 7.3.2.Sugar Cane
- 7.3.3.Sweet Sorghum
- 7.4.Cellulosic Materials
- 7.4.1.Crop Residues
- 7.4.1.1.Straw
- 7.4.1.2.Corn Stover
- 7.4.1.3.Bagasse
- 7.4.2.Wood/Forest Residues
- 7.4.3.Dedicated Energy Crops
- 7.4.3.1.Willow
- 7.4.3.2.Poplar
- 7.4.3.3.Switchgrass
- 7.4.4.Industrial and Other Wastes
- 7.4.1.Crop Residues
8.By Generation
- 8.1.Introduction
- 8.1.1.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Generation
- 8.1.2.Market Attractiveness Index, By Generation
- 8.2.First Generation*
- 8.2.1.Introduction
- 8.2.2.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%)
- 8.3.Second Generation
- 8.4.Third Generation
9.By Fuel Type
- 9.1.Introduction
- 9.1.1.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Fuel Type
- 9.1.2.Market Attractiveness Index, By Fuel Type
- 9.2.Traditional*
- 9.2.1.Introduction
- 9.2.2.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%)
- 9.3.Bioethanol
- 9.3.1.E5
- 9.3.2.E10
- 9.3.3.E15 to E70
- 9.3.4.E75 to E85
- 9.3.5.Others
10.By End-User
- 10.1.Introduction
- 10.1.1.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By End-User
- 10.1.2.Market Attractiveness Index, By End-User
- 10.2.Automotive*
- 10.2.1.Introduction
- 10.2.2.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%)
- 10.3.Food and Beverage
- 10.4.Pharmaceuticals
- 10.5.Cosmetics
- 10.6.Fuel Cells
- 10.7.Fertilizers
- 10.8.Pesticides
- 10.9.Industrial Solvent
- 10.10.Others
11.By Region
- 11.1.Introduction
- 11.1.1.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Region
- 11.1.2.Market Attractiveness Index, By Region
- 11.2.North America
- 11.2.1.Introduction
- 11.2.2.Key Region-Specific Dynamics
- 11.2.3.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Feedstock
- 11.2.4.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Generation
- 11.2.5.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Fuel Type
- 11.2.6.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By End-User
- 11.2.7.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Country
- 11.2.7.1.U.S.
- 11.2.7.2.Canada
- 11.2.7.3.Mexico
- 11.3.Europe
- 11.3.1.Introduction
- 11.3.2.Key Region-Specific Dynamics
- 11.3.3.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Feedstock
- 11.3.4.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Generation
- 11.3.5.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Fuel Type
- 11.3.6.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By End-User
- 11.3.7.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Country
- 11.3.7.1.Germany
- 11.3.7.2.UK
- 11.3.7.3.France
- 11.3.7.4.Italy
- 11.3.7.5.Russia
- 11.3.7.6.Rest of Europe
- 11.4.South America
- 11.4.1.Introduction
- 11.4.2.Key Region-Specific Dynamics
- 11.4.3.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Feedstock
- 11.4.4.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Generation
- 11.4.5.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Fuel Type
- 11.4.6.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By End-User
- 11.4.7.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Country
- 11.4.7.1.Brazil
- 11.4.7.2.Argentina
- 11.4.7.3.Rest of South America
- 11.5.Asia-Pacific
- 11.5.1.Introduction
- 11.5.2.Key Region-Specific Dynamics
- 11.5.3.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Feedstock
- 11.5.4.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Generation
- 11.5.5.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Fuel Type
- 11.5.6.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By End-User
- 11.5.7.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Country
- 11.5.7.1.China
- 11.5.7.2.India
- 11.5.7.3.Japan
- 11.5.7.4.Australia
- 11.5.7.5.Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 11.6.Middle East and Africa
- 11.6.1.Introduction
- 11.6.2.Key Region-Specific Dynamics
- 11.6.3.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Feedstock
- 11.6.4.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Generation
- 11.6.5.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Fuel Type
- 11.6.6.Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By End-User
12.Competitive Landscape
- 12.1.Competitive Scenario
- 12.2.Market Positioning/Share Analysis
- 12.3.Mergers and Acquisitions Analysis
13.Company Profiles
- 13.1.ADM*
- 13.1.1.Company Overview
- 13.1.2.Product Portfolio and Description
- 13.1.3.Financial Overview
- 13.1.4.Key Developments
- 13.2.Cargill, Incorporated
- 13.3.Solvay
- 13.4.Mitsubishi Chemical Company
- 13.5.Heineken
- 13.6.AB Miller
- 13.7.British Petroleum
- 13.8.The Andersons Inc.
- 13.9.Advanced Bioenergy LLC
- 13.10.Stake Technology
LIST NOT EXHAUSTIVE
14.Appendix
- 14.1.About Us and Services
- 14.2.Contact Us