|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1325374
スクラップの世界市場-2023年~2030年Global Scrap Market - 2023-2030 |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| スクラップの世界市場-2023年~2030年 |
|
出版日: 2023年08月04日
発行: DataM Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 190 Pages
納期: 即日から翌営業日
|
- 全表示
- 概要
- 目次
市場概要
世界のスクラップ市場は、2022年に8,720万米ドルに達し、2030年には1億9,690万米ドルに達すると予測され、予測期間2023-2030年のCAGRは16.5%で成長する見込みです。
世界のスクラップ市場とは、金属、紙、プラスチック、電子廃棄物などの廃棄物の国際取引とリサイクルを指します。スクラップ市場は、二次原料の需要と供給をつなぐ重要な役割を担っています。世界スクラップ市場は国際経済の重要な構成要素として台頭し、資源保護、持続可能性、経済成長において極めて重要な役割を果たしています。環境責任への注目が高まる中、スクラップ産業は世界のサプライチェーンにおける重要なプレーヤーとして重要性を増しています。
スクラップ市場では非鉄部門が急成長を遂げており、市場シェアの半分以上を占めています。成長の加速は、リサイクル技術の大幅な技術的進歩と金属価格の変動の増大によるものです。アジア太平洋はスクラップ市場で最大の市場シェアを占めており、市場全体の3分の1以上を占めています。同地域の優位性は主に、同地域の建設活動を促進するインフラの拡大、工業化、都市化に拠ります。
市場力学
循環型経済への注目の高まり
近年、循環型経済の概念は、環境と経済の課題に対する持続可能な解決策として、世界中で大きな支持を得ています。リサイクル、リユース、廃棄物削減の原則を推進することで、循環型経済は、資源の消費を最小限に抑え、ライフサイクル全体を通じて素材の価値を最大化することを目指しています。
循環型経済の枠組みは、企業や個人が持続可能な慣行を採用することを奨励し、資源の管理や廃棄物の捉え方を根本的に変えることにつながります。それぞれの焦点の転換は、様々な産業、特にスクラップ市場に大きな影響を与えています。
さらに、政府や組織は世界的に、廃棄物の削減、資源の節約、環境への影響の最小化の重要性を認識しつつあります。循環型経済は、クローズドループ・システムを構築するために、素材の再利用とリサイクルを重視します。エレン・マッカーサー財団によると、循環型経済は2030年までに年間2兆6,000億米ドルの利益を生み出す可能性があります。循環型経済への各方面からの働きかけは、様々な産業にとって貴重な投入材料としてのスクラップ需要を押し上げています。
環境意識の高まりとリサイクル技術の進歩
環境への関心の高まりと持続可能な実践の必要性が、スクラップ需要を後押ししています。各国政府はリサイクルを促進し、廃棄物の発生を減らすための規制と政策を実施しています。例えば、欧州連合(EU)の廃棄物枠組み指令は、加盟国にリサイクル目標を設定し、2025年までに都市廃棄物の55%リサイクルを目指しています。
また、政府は企業や消費者に対し、リサイクルやリサイクル素材の使用など、持続可能な慣行を採用するよう奨励します。持続可能性に向けたそれぞれの後押しが、リサイクル製品の原料としてのスクラップ需要を生み出しています。さらに、リサイクルプロセスにおける技術的進歩が、世界のスクラップ市場を牽引する上で重要な役割を果たしています。選別、分離、精製技術の革新により、スクラップから貴重な材料を回収することがより現実的になっています。
熱分解やケミカルリサイクルなどの高度なリサイクル技術は、リサイクル可能な材料の範囲を広げ、リサイクル製品の品質を向上させました。国際固形廃棄物協会(ISWA)によると、世界の廃棄物エネルギー化能力は2020年に年間3億6,700万トンに達し、これは高度廃棄物管理技術の採用増加を反映しています。
規制上の障壁とインフラ・技術進歩の欠如
世界のスクラップ市場に影響を与える主な抑制要因のひとつは、複雑で一貫性のない規制の存在です。こうした規制は国や地域によって異なるため、国境を越えたスクラップ原料の円滑な移動に障壁が生じています。輸出入規制、ライセンス要件、環境規制はスクラップ業者にとってしばしば課題となり、市場機会を制限し、運営コストを増加させます。
世界貿易機関(WTO)によると、2021年時点でスクラップ原料の世界貿易の約40%が何らかの輸入制限や規制措置の対象となっています。世界のスクラップ市場が直面するもう一つの重大な抑制要因は、スクラップ原料の収集、選別、処理のためのインフラが不十分なことです。不十分なリサイクル施設と時代遅れの技術が、世界的に増加するスクラップ発生量を効率的に処理する業界の能力を妨げています。
国際資源パネル(IRP)のデータによると、2020年時点で、世界で発生するスクラップのうち、効果的にリサイクルされているのは39%に過ぎません。このような障壁はスクラップ市場の効率性と収益性に悪影響を及ぼし、取引量の減少と世界市場へのアクセスの制限につながります。
COVID-19影響分析
COVID-19の大流行は、世界経済のさまざまな分野に広範囲に及ぶ影響を及ぼしました。COVID-19は世界のサプライチェーンに広範な混乱を引き起こし、スクラップ原料の入手と流通に影響を与えました。各国のデータから、操業停止、渡航制限、産業活動の縮小により、スクラップの収集、加工、取引活動が大幅に減少したことが明らかになっています。例えば、公式報告によると、2020年のスクラップ回収率は世界全体で前年比平均20%減少しました。
さらに、パンデミックは工業生産の急激な減少につながり、その結果、スクラップ原料の需要が減少しました。製造施設の閉鎖とそれに続く建設活動の鈍化は、金属スクラップ、プラスチック、その他のリサイクル可能な材料の需要に悪影響を与えました。
情報筋によれば、2020年の世界の金属スクラップ需要は約25%減少し、在庫余剰と価格変動につながっています。今後、パンデミック後の世界における世界スクラップ市場の回復と持続可能性を支えるためには、政府、企業、利害関係者の協調努力が必要です。
目次
第1章 調査手法と調査範囲
第2章 定義と概要
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場力学
- 影響要因
- 促進要因
- 循環型経済への注目の高まり
- 環境意識の高まりとリサイクル技術の進歩
- 抑制要因
- 規制上の障壁、インフラと技術進歩の欠如
- 機会
- 影響分析
- 促進要因
第5章 産業分析
- ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- サプライチェーン分析
- 価格分析
- 規制分析
第6章 COVID-19分析
第7章 金属別
- 鉄
- 非鉄
第8章 タイプ別
- リサイクル
- ゴミ
- 廃棄物
第9章 発生源別
- 缶
- 端材
- 不合格部品
- その他
第10章 エンドユーザー別
- 建設
- 自動車
- 造船
- 機械製造
- 家電
- その他
第11章 地域別
- 北米
- 米国
- カナダ
- メキシコ
- 欧州
- ドイツ
- 英国
- フランス
- イタリア
- ロシア
- その他欧州
- 南米
- ブラジル
- アルゼンチン
- その他南米
- アジア太平洋
- 中国
- インド
- 日本
- オーストラリア
- その他アジア太平洋
- 中東・アフリカ
第12章 競合情勢
- 競合シナリオ
- 市況/シェア分析
- M&A分析
第13章 企業プロファイル
- ArcelorMittal
- 会社概要
- 製品ポートフォリオと説明
- 財務概要
- 主な動向
- Nucor Corporation
- Commercial Metals Company
- Sims Metal Management Limited
- Aurubis AG
- Stena Metall AB
- Tetronics Limited
- Waste Management, Inc.
- Enviro-Hub Holdings Limited
- BOLIDEN AB
第14章 付録
Market Overview
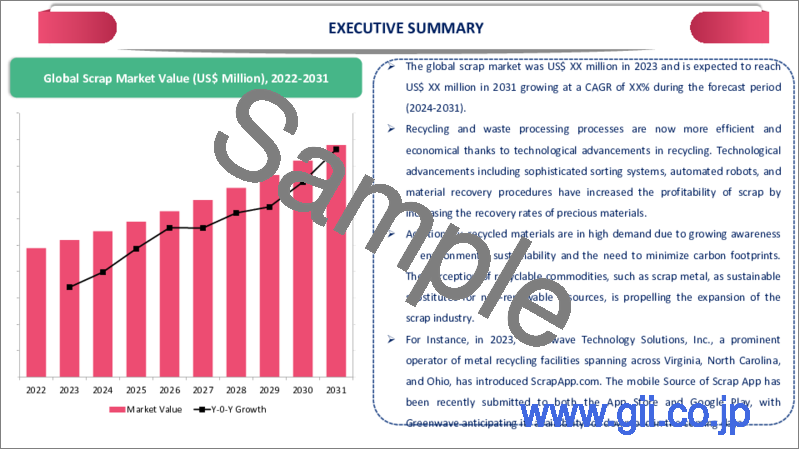
Global Scrap Market reached US$ 87.2 million in 2022 and is expected to reach US$ 196.9 million by 2030, growing with a CAGR of 16.5 % during the forecast period 2023-2030.
The global scrap market refers to the international trade and recycling of discarded materials, including metals, paper, plastics, and electronic waste. It functions as a critical link between the supply and demand for secondary raw materials. The global scrap market has emerged as a crucial component of the international economy, playing a pivotal role in resource conservation, sustainability, and economic growth. With the increasing focus on environmental responsibility, the scrap industry has gained significance as a key player in the global supply chain.
The non-ferrous segment is witnessing rapid growth within the scrap market, capturing more than half of the market share. The accelerated growth can be attributed to significant technological advancements recycling technologies and increasing volatility in metal prices. Asia-Pacific holds the largest market share in the scrap market, accounting for over one-third of the total market. The region's dominance is primarily driven by the expanding infrastructure, industrialization and urbanization that promotes construction activities in the region.
Market Dynamics
Increasing focus on circular economy
In recent years, the concept of a circular economy has gained significant traction worldwide as a sustainable solution to environmental and economic challenges. By promoting the principles of recycling, reusing, and reducing waste, the circular economy aims to minimize resource consumption and maximize the value of materials throughout their lifecycle.
The circular economy framework encourages businesses and individuals to adopt sustainable practices, leading to a fundamental change in the way resources are managed and waste is perceived. The respective shift in focus has had a profound impact on various industries, particularly the scrap market.
Further, governments and organizations globally are increasingly recognizing the importance of reducing waste, conserving resources, and minimizing environmental impact. The circular economy emphasizes the reuse and recycling of materials to create a closed-loop system. According to the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, the circular economy could generate a benefit of US$ 2.6 trillion annually by 2030. The respective drive towards circularity has boosted the demand for scraps as valuable input materials for various industries.
Growing Environmental Awareness and Advancements in Recycling Technologies
Rising environmental concerns and the need for sustainable practices have propelled the demand for scraps. Governments have implemented regulations and policies to promote recycling and reduce waste generation. For instance, the European Union's Waste Framework Directive sets recycling targets for member states, aiming for 55% recycling of municipal waste by 2025.
Governments also incentivize businesses and consumers to adopt sustainable practices, such as recycling and using recycled materials. The respective push towards sustainability has created a demand for scraps as feedstock for recycled products. Moreover, the technological advancements in recycling processes have played a crucial role in driving the global scraps market. Innovations in sorting, separation, and purification technologies have made it more feasible to recover valuable materials from scraps.
Advanced recycling techniques, such as pyrolysis and chemical recycling, have expanded the range of recyclable materials and improved the quality of recycled products. According to the International Solid Waste Association (ISWA), global waste-to-energy capacity reached 367 million tons per year in 2020, reflecting an increase in the adoption of advanced waste management technologies.
Regulatory Barriers and Lack of Infrastructure and Technological Advancements
One of the primary restraints affecting the global scrap market is the presence of complex and inconsistent regulations. Such regulations vary across countries and regions, creating barriers to the smooth movement of scrap materials across borders. Export and import restrictions, licensing requirements, and environmental regulations often pose challenges for scrap traders, limiting market opportunities and increasing operational costs.
According to the World Trade Organization (WTO), as of 2021, approximately 40% of global trade in scrap materials was subject to some form of import restrictions or regulatory measures. Another significant restraint faced by the global scrap market is the inadequate infrastructure for the collection, sorting, and processing of scrap materials. Insufficient recycling facilities and outdated technologies hamper the industry's ability to efficiently handle the growing volume of scrap generated globally.
Data from the International Resource Panel (IRP) indicates that as of 2020, only 39% of global scrap generated was effectively recycled, primarily due to limited infrastructure and technological advancements. Such barriers adversely affect the efficiency and profitability of the scrap market, leading to reduced trade volumes and limited access to global markets.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis
The COVID-19 pandemic has had far-reaching consequences across various sectors of the global economy. COVID-19 caused widespread disruptions in global supply chains, affecting the availability and distribution of scrap materials. Data from various countries reveals a significant decline in scrap collection, processing, and trading activities due to lockdowns, travel restrictions, and reduced industrial operations. For example, according to official reports, the scrap collection rate dropped by an average of 20% globally in 2020 compared to the previous year.
Further, the pandemic led to a sharp decline in industrial production, resulting in decreased demand for scrap materials. The closure of manufacturing facilities and the subsequent slowdown in construction activities negatively impacted the demand for metal scrap, plastics, and other recyclable materials.
Sources report a decline of approximately 25% in the global demand for scrap metal in 2020, leading to a surplus in inventories and price volatility. Moving forward, concerted efforts from governments, businesses, and stakeholders are needed to support the recovery and sustainability of the global scrap market in a post-pandemic world.
Segment Analysis
The global automotive oem coatings market is segmented based on metal, type, source, end-user and region.
The Increasing Adoption of Sustainable Practices and The Concept of a Circular Economy
The increasing adoption of sustainable practices and the concept of a circular economy have contributed to the growth of the non-ferrous segment, particularly aluminum scraps. Industries are recognizing the value of recycling and reusing materials to reduce waste and conserve resources. Aluminum scraps play a vital role in the circular economy by providing a source of secondary raw material for the production of new aluminum products. The World Economic Forum estimates that the circular economy for aluminum could generate US$ 40 billion annually by 2030.
Moreover, government initiatives and regulations play a significant role in driving the growth of the non-ferrous segment, specifically aluminum scraps. Governments globally are implementing policies to promote recycling and reduce the environmental impact of metal production. For instance, the European Union's Circular Economy Action Plan sets a target of 50% aluminum recycling by 2030. The aforementioned growth in emphasis on sustainability and the circular economy drives the demand for aluminum scraps in the global scrap market.
Geographical Analysis
Rapid Industrialization and Urbanization, Leading to Increased Consumption and Generation of Scrap Materials
The scrap market plays a vital role in the global economy, providing a sustainable source of raw materials for various industries. Asia-Pacific has undergone rapid industrialization and urbanization, leading to increased consumption and generation of scrap materials. As economies in the region continue to grow, there is a rising demand for raw materials to support construction, manufacturing, and infrastructure development. According to data from the Asian Development Bank (ADB), Asia's share of global GDP reached 46.5% in 2020, reflecting the region's economic significance.
Moreover, infrastructure development projects, such as roads, bridges, and buildings, require substantial quantities of raw materials, including scrap metals. Asia-Pacific has witnessed a surge in infrastructure investments, driven by government initiatives to enhance connectivity and stimulate economic growth. Asia-Pacific has emerged as a significant player in the global scrap market, experiencing remarkable growth in recent years. The respective growth has contributed to the expansion of the scrap market in Asia-Pacific.
Competitive Landscape
The major global players in the market include ArcelorMittal, Nucor Corporation, Commercial Metals Company, Sims Metal Management Limited, Aurubis AG, Stena Metall AB, Tetronics Limited, Waste Management, Inc., Enviro-Hub Holdings Limited and BOLIDEN AB.
Why Purchase the Report?
- To visualize the global scrap market segmentation based on metal, type, source, end-user and region, as well as understand key commercial assets and players.
- Identify commercial opportunities by analyzing trends and co-development.
- Excel data sheet with numerous data points of scrap market-level with all segments.
- PDF report consists of a comprehensive analysis after exhaustive qualitative interviews and an in-depth study.
- Product mapping available as excel consisting of key products of all the major players.
The global scrap market report would provide approximately 69 tables, 69 figures and 190 Pages.
Target Audience 2023
- Manufacturers/ Buyers
- Industry Investors/Investment Bankers
- Research Professionals
- Emerging Companies
Table of Contents
1. Methodology and Scope
- 1.1. Research Methodology
- 1.2. Research Objective and Scope of the Report
2. Definition and Overview
3. Executive Summary
- 3.1. Snippet by Metal
- 3.2. Snippet by Type
- 3.3. Snippet by Source
- 3.4. Snippet by End-User
- 3.5. Snippet by Region
4. Dynamics
- 4.1. Impacting Factors
- 4.1.1. Drivers
- 4.1.1.1. Increasing focus on Circular Economy
- 4.1.1.2. Growing Environmental Awareness and Advancements in Recycling Technologies
- 4.1.2. Restraints
- 4.1.2.1. Regulatory Barriers and Lack of Infrastructure and Technological Advancements
- 4.1.3. Opportunity
- 4.1.4. Impact Analysis
- 4.1.1. Drivers
5. Industry Analysis
- 5.1. Porter's Five Force Analysis
- 5.2. Supply Chain Analysis
- 5.3. Pricing Analysis
- 5.4. Regulatory Analysis
6. COVID-19 Analysis
- 6.1. Analysis of COVID-19
- 6.1.1. Scenario Before COVID
- 6.1.2. Scenario During COVID
- 6.1.3. Scenario Post COVID
- 6.2. Pricing Dynamics Amid COVID-19
- 6.3. Demand-Supply Spectrum
- 6.4. Government Initiatives Related to the Market During Pandemic
- 6.5. Manufacturers Strategic Initiatives
- 6.6. Conclusion
7. By Metal
- 7.1. Introduction
- 7.1.1. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Metal
- 7.1.2. Market Attractiveness Index, By Metal
- 7.2. Ferrous*
- 7.2.1. Introduction
- 7.2.2. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%)
- 7.3. Non-Ferrous
8. By Type
- 8.1. Introduction
- 8.1.1. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Type
- 8.1.2. Market Attractiveness Index, By Type
- 8.2. Recycled*
- 8.2.1. Introduction
- 8.2.2. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%)
- 8.3. Trashed
- 8.4. Disposed
9. By Source
- 9.1. Introduction
- 9.1.1. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Source
- 9.1.2. Market Attractiveness Index, By Source
- 9.2. Cans*
- 9.2.1. Introduction
- 9.2.2. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%)
- 9.3. Offcuts
- 9.4. Rejected Parts
- 9.5. Others
10. By End-User
- 10.1. Introduction
- 10.1.1. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By End-User
- 10.1.2. Market Attractiveness Index, By End-User
- 10.2. Construction*
- 10.2.1. Introduction
- 10.2.2. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%)
- 10.3. Automotive
- 10.4. Shipbuilding
- 10.5. Equipment Manufacturing
- 10.6. Consumer Appliances
- 10.7. Others
11. By Region
- 11.1. Introduction
- 11.1.1. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Region
- 11.1.2. Market Attractiveness Index, By Region
- 11.2. North America
- 11.2.1. Introduction
- 11.2.2. Key Region-Specific Dynamics
- 11.2.3. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Metal
- 11.2.4. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Type
- 11.2.5. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Source
- 11.2.6. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By End-User
- 11.2.7. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Country
- 11.2.7.1. U.S.
- 11.2.7.2. Canada
- 11.2.7.3. Mexico
- 11.3. Europe
- 11.3.1. Introduction
- 11.3.2. Key Region-Specific Dynamics
- 11.3.3. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Metal
- 11.3.4. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Type
- 11.3.5. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Source
- 11.3.6. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By End-User
- 11.3.7. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Country
- 11.3.7.1. Germany
- 11.3.7.2. UK
- 11.3.7.3. France
- 11.3.7.4. Italy
- 11.3.7.5. Russia
- 11.3.7.6. Rest of Europe
- 11.4. South America
- 11.4.1. Introduction
- 11.4.2. Key Region-Specific Dynamics
- 11.4.3. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Metal
- 11.4.4. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Type
- 11.4.5. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Source
- 11.4.6. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By End-User
- 11.4.7. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Country
- 11.4.7.1. Brazil
- 11.4.7.2. Argentina
- 11.4.7.3. Rest of South America
- 11.5. Asia-Pacific
- 11.5.1. Introduction
- 11.5.2. Key Region-Specific Dynamics
- 11.5.3. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Metal
- 11.5.4. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Type
- 11.5.5. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Source
- 11.5.6. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By End-User
- 11.5.7. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Country
- 11.5.7.1. China
- 11.5.7.2. India
- 11.5.7.3. Japan
- 11.5.7.4. Australia
- 11.5.7.5. Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 11.6. Middle East and Africa
- 11.6.1. Introduction
- 11.6.2. Key Region-Specific Dynamics
- 11.6.3. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Metal
- 11.6.4. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Type
- 11.6.5. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Source
- 11.6.6. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By End-User
12. Competitive Landscape
- 12.1. Competitive Scenario
- 12.2. Market Positioning/Share Analysis
- 12.3. Mergers and Acquisitions Analysis
13. Company Profiles
- 13.1. ArcelorMittal*
- 13.1.1. Company Overview
- 13.1.2. Product Portfolio and Description
- 13.1.3. Financial Overview
- 13.1.4. Key Developments
- 13.2. Nucor Corporation
- 13.3. Commercial Metals Company
- 13.4. Sims Metal Management Limited
- 13.5. Aurubis AG
- 13.6. Stena Metall AB
- 13.7. Tetronics Limited
- 13.8. Waste Management, Inc.
- 13.9. Enviro-Hub Holdings Limited
- 13.10. BOLIDEN AB
LIST NOT EXHAUSTIVE
14. Appendix
- 14.1. About Us and Services
- 14.2. Contact Us