|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1665951
分子接着剤の世界市場:競合情勢(2025年)Molecular Glues - Competitive landscape, 2025 |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 分子接着剤の世界市場:競合情勢(2025年) |
|
出版日: 2025年03月01日
発行: DelveInsight
ページ情報: 英文 180 Pages
納期: 2~10営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 図表
- 目次
分子接着剤(MG)化合物は、その結合後に標的タンパク質を分解、安定化、あるいは活性化することにより、タンパク質間相互作用(PPI)やインタラクトームを変化させることができるユニークな低分子化合物の一種です。このような低分子MGは、がんを含むヒト疾患の治療に応用できる可能性があることが徐々に認識されつつあります。その証拠に、低分子MG化合物は本質的に、ヒト疾患の病因において重要な役割を果たすあらゆるタンパク質を標的とし得ることが示唆されており、これらのタンパク質標的の多くは、以前は治療不可能と考えられていました。興味深いことに、がん治療に高い効果を示す低分子MG化合物の多くは、複数の主要なタンパク質を標的としています。一方、一つの標的タンパク質が、異なる化学構造を持つ複数のMG化合物によって接着されることもあります。MG-タンパク質相互作用プロファイルの高い柔軟性は、疾患メカニズムの解明に役立つ分子ツールとして使用できる低分子MG化合物の成長と開発のための豊かな土壌を提供し、ヒト疾患、特にヒトがんの治療のための薬剤開発を促進することもできます。
MG化合物は、その作用機序や標的によって様々なタイプに分類することができます。ひとつはサリドマイドのような免疫調節イミド薬(IMiD)で、E3リガーゼをリクルートして特定の基質を分解します。もう一つのタイプは、標的タンパク質とユビキチンリガーゼの接近を誘導し、効果的に標的を分解するように設計された合成低分子化合物です。さらに、ラパマイシンのような天然物由来の分子グルーは、特定のタンパク質に結合し、他の細胞機構との相互作用を橋渡しすることによって機能します。これらの多様なタイプの分子グルーは、特に治療不可能なタンパク質を標的とした治療への応用に大きな可能性を秘めています。
分子接着剤は、タンパク質の相互作用を調節することにより、様々な疾患の治療に大きな可能性を示します。がん治療では、IMiD(サリドマイドやその誘導体など)のような分子グルーを用いて、がん化タンパク質の分解を誘導し、がん細胞を選択的に除去する戦略を提供してきました。これらの分子は、がん細胞の生存と増殖に重要な転写因子やその他のタンパク質を標的としています。神経変性疾患の領域では、アルツハイマー病やパーキンソン病などの病態に関与するタウやα-シヌクレインのような、ミスフォールディングあるいは凝集したタンパク質の分解を促進するように分子接着剤を設計することができます。タンパク質間の相互作用を変化させることにより、分子接着剤は有害タンパク質の蓄積を緩和する新しい治療法を提供し、それによって病気の進行を遅らせ、症状を緩和する可能性があります。これらの応用は、標的タンパク質の調節を通じて複雑な疾患に対処する分子グルーの多様性と将来性を強調するものです。
当レポートでは、世界の分子接着剤市場について調査し、市場の概要とともに、競合情勢、参入各社の概要と主な製品開発動向などを提供しています。
目次
イントロダクション
エグゼクティブサマリー
分子接着剤:概要
- イントロダクション
- 分類
- 作用機序
- ターゲット
- 応用
分子接着剤- 分析的視点:徹底的な商業的評価
- 分子接着剤のコラボレーション分析、企業別
競合情勢
- 企業の比較評価(治療法、開発段階、技術別)
治療評価
- 製品タイプ別の評価
- 段階別、製品タイプ別の評価
- 投与経路別の評価
- 段階別、投与経路別の評価
- 分子タイプ別の評価
- 段階別、分子タイプ別の評価
分子接着剤:企業および製品プロファイル(上市済み治療法)
Bristol Myers Squibb
レブラミド
分子接着剤:企業および製品プロファイル(パイプライン治療)
後期段階の製品(第III相)
Bristol Myers Squibb
ゴルカドミド
中期段階の製品(第II相)
初期段階の製品(第I相)
Nested Therapeutics
NST-628
前臨床および創薬段階の製品
非アクティブな製品
分子接着剤-アンメットニーズ
分子接着剤-市場促進要因と抑制要因
List of Tables
- Table 1 Total Products for Molecular Glues
- Table 2 Late Stage Products
- Table 3 Mid Stage Products
- Table 4 Early Stage Products
- Table 5 Pre-clinical & Discovery Stage Products
- Table 6 Assessment by Product Type
- Table 7 Assessment by Stage and Product Type
- Table 8 Assessment by Route of Administration
- Table 9 Assessment by Stage and Route of Administration
- Table 10 Assessment by Molecule Type
- Table 11 Assessment by Stage and Molecule Type
- Table 12 Inactive Products
List of Figures
- Figure 1 Total Products for Molecular Glues
- Figure 2 Late Stage Products
- Figure 3 Mid Stage Products
- Figure 4 Early Stage Products
- Figure 5 Preclinical and Discovery Stage Products
- Figure 6 Assessment by Product Type
- Figure 7 Assessment by Stage and Product Type
- Figure 8 Assessment by Route of Administration
- Figure 9 Assessment by Stage and Route of Administration
- Figure 10 Assessment by Molecule Type
- Figure 11 Assessment by Stage and Molecule Type
- Figure 12 Inactive Products
DelveInsight's, "Molecular Glues - Competitive landscape, 2025," report provides comprehensive insights about 50+ companies and 65+ drugs in Molecular Glues Competitive landscape. It covers the therapeutics assessment by product type, stage, route of administration, and molecule type. It further highlights the inactive pipeline products in this space.
Geography Covered:
- Global coverage
Molecular Glues: Understanding
Molecular Glues: Overview
Molecular glue (MG) compounds are a type of unique small molecule that can change the protein-protein interactions (PPIs) and interactomes by degrading, stabilizing, or activating the target protein after their binging. These small-molecule MGs are gradually being recognized for their potential application in treating human diseases, including cancer. Evidence suggests that small-molecule MG compounds could essentially target any proteins, which play critical roles in human disease etiology, where many of these protein targets were previously considered undruggable. Intriguingly, most MG compounds with high efficacy for cancer treatment can glue on and control multiple key protein targets. On the other hand, a single key protein target can also be glued by multiple MG compounds with distinct chemical structures. The high flexibility of MG-protein interaction profiles provides rich soil for the growth and development of small-molecule MG compounds that can be used as molecular tools to assist in unraveling disease mechanisms, and they can also facilitate drug development for the treatment of human disease, especially human cancer.
They can be classified into different types based on their mechanisms and targets. One type includes immunomodulatory imide drugs (IMiDs) like thalidomide, which recruit E3 ligases to degrade specific substrates. Another type encompasses synthetic small molecules designed to induce proximity between target proteins and ubiquitin ligases, effectively marking the target for degradation. Additionally, natural product-derived molecular glues, such as rapamycin, function by binding to specific proteins and bridging their interaction with other cellular machinery. These diverse types of molecular glues have significant potential for therapeutic applications, especially in targeting undruggable proteins.
Molecular glues exhibit significant potential in treating a variety of diseases by modulating protein interactions. In cancer therapy, molecular glues such as IMiDs (e.g., thalidomide and its derivatives) have been employed to induce the degradation of oncogenic proteins, providing a strategy to eliminate cancer cells selectively. These molecules target transcription factors and other proteins crucial for cancer cell survival and proliferation. In the realm of neurodegenerative diseases, molecular glues can be designed to promote the degradation of misfolded or aggregated proteins, such as tau or alpha-synuclein, which are implicated in conditions like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. By altering protein-protein interactions, molecular glues offer a novel therapeutic approach to mitigate the accumulation of toxic proteins, thereby potentially slowing disease progression and alleviating symptoms. These applications underscore the versatility and promise of molecular glues in addressing complex diseases through targeted protein modulation.
Report Highlights:
- In May 2024, Takeda Pharmaceuticals announced an exclusive licensing deal with China-based Degron Therapeutics to develop novel molecular glue degraders for various oncology, neuroscience and inflammatory disease targets.
- In May 2024, NEOsphere Biotechnologies GmbH announced a collaboration with Kymera Therapeutics, Inc. focused on unlocking undrugged or poorly drugged disease-causing protein targets that can be only or best addressed by Targeted Protein Degradation. Under the agreement, NEOsphere Biotechnologies will utilize its target- and E3-agnostic platform to screen molecular glue compounds on a proteome-wide level and in a native context.
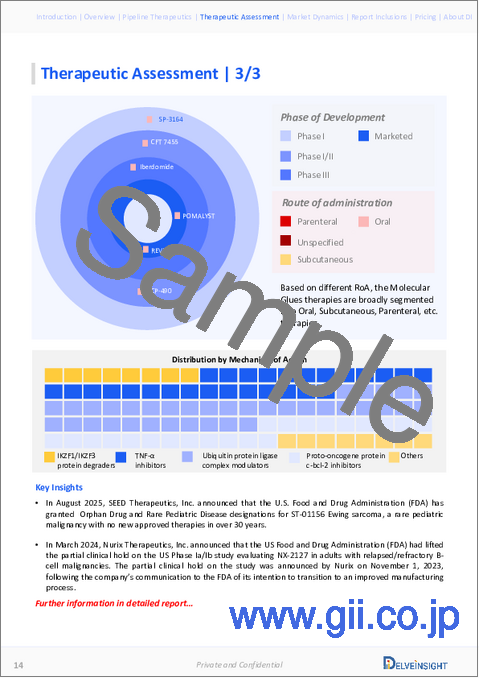
- In March 2024, Nurix Therapeutics, Inc. announced that the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had lifted the partial clinical hold on the U.S. Phase Ia/Ib study evaluating NX-2127 in adults with relapsed/refractory B-cell malignancies. The partial clinical hold on the study was announced by Nurix on November 1, 2023, following the company's communication to the FDA of its intention to transition to an improved manufacturing process.
- In February 2024, Neomorph, Inc. announced about collaboration and licensing agreement with global healthcare company Novo Nordisk to discover, develop and commercialize molecular glue degraders. Under the terms of the deal, Neomorph will lead discovery and preclinical activities against unnamed selected targets. Novo Nordisk will then have the option to exclusively pursue further clinical development and commercialization of the compounds.
- In September 2023, Orionis Biosciences, a privately held life sciences company with an integrated drug discovery and chemical biology platform, announced a multi-year collaboration with Genentech, a member of the Roche Group, to discover novel small molecule medicines for challenging targets in major disease areas, including oncology and neurodegeneration. Under the terms of the agreement, Orionis will be responsible for the discovery and optimization of molecular glues for Genentech's designated targets, while Genentech will be responsible for subsequent later-stage preclinical, clinical development, regulatory filing, and commercialization of such small molecules.
Molecular Glues: Company and Product Profiles (Marketed)
1. Company Overview: Bristol Myers Squibb
Bristol Myers Squibb is a global biopharmaceutical company that focuses on discovering, developing, and delivering innovative medicines to patients with serious diseases. Headquartered in New York City, the company specializes in areas such as oncology, immunology, cardiovascular diseases, and fibrosis. Through extensive research and development efforts, Bristol Myers Squibb aims to address unmet medical needs and improve the quality of life for patients around the world. The company collaborates with various partners and employs advanced scientific methods to advance its pipeline of therapeutics.
Product Description: REVLIMID
REVLIMID is a prescription medicine, used to treat adults with multiple myeloma (MM) in combination with the medicine dexamethasone, or as maintenance treatment after autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (a type of stem cell transplant that uses your own stem cells). REVLIMID should not be used to treat people who have chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) unless they are participants in a controlled clinical trial. It is not known if REVLIMID is safe and effective in children.
Product Description: POMALYST
POMALYST is a prescription medicine used to treat adults with Multiple myeloma, taken along with the medicine dexamethasone, in patients who have previously received at least 2 medicines to treat multiple myeloma, including a proteasome inhibitor and lenalidomide, and whose disease has become worse during treatment or within 60 days of finishing the last treatment. It is not known if POMALYST is safe and effective in children.
Molecular Glues: Company and Product Profiles (Pipeline)
1. Company Overview: Bristol Myers Squibb
Bristol Myers Squibb is a global biopharmaceutical company that focuses on discovering, developing, and delivering innovative medicines to patients with serious diseases. Headquartered in New York City, the company specializes in areas such as oncology, immunology, cardiovascular diseases, and fibrosis. Through extensive research and development efforts, Bristol Myers Squibb aims to address unmet medical needs and improve the quality of life for patients around the world. The company collaborates with various partners and employs advanced scientific methods to advance its pipeline of therapeutics.
Product Description: Golcadomide
Golcadomide (CC-99282) is an oral molecular glue that promotes degradation of IKZF1/3 transcription factors (Ikaros/Aiolos) by engaging the cereblon E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. Structurally golcadomide is a novel thalidomide analogue (known as a CELMoD/cereblon E3 ligase modulator). It has immunomodulatory actions, with enhanced antiproliferative and proapoptotic activities. Currently, Golcadomide is in Phase III stage of development for the treatment of B-cell Lymphoma.
2. Company Overview: Revolution Medicines, Inc.
Revolution Medicines is a biopharmaceutical company focused on developing targeted cancer therapies that inhibit frontier oncology targets, particularly RAS proteins. The company's mission is to revolutionize treatment for patients with RAS-addicted cancers, which account for a significant portion of lung, colorectal, and pancreatic cancer cases. Revolution Medicines has a pipeline of novel RAS(ON) inhibitors and RAS companion inhibitors designed to permanently disengage the "ON" switch of mutated RAS proteins and suppress cooperating pathways that sustain RAS-addicted cancers.
Product Description: RMC 6291
RMC-6291 is an orally active and covalent inhibitor of KRASG12C(ON). RMC-6291 forms a tri-complex within tumor cells between KRASG12C(ON) and cyclophilin A (CypA). Thus, RMC-6291 prevents KRASG12C(ON) from signaling via steric blockade of RAS effector binding. RMC-6291 inhibits ERK signaling and induced apoptosis in KRASG12C-mutant H358 cells. RMC-6291 also inhibits the proliferation of KRASG12C mutant cells with a median IC50 of 0.11 nM. RMC-6291 may address an area of high unmet need for patients with KRAS G12C-mutant advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and colorectal cancer (CRC), including patients with NSCLC whose disease has progressed on prior treatment with other KRAS G12C(OFF) inhibitors. Currently, RMC-6291 is in Phase I/II stage of development for the treatment of Solid tumors including NSCLC and SCLC.
3. Company Overview: Nested Therapeutics
Nested Therapeutics is a biotechnology company focused on discovering and developing novel, targeted, small molecule precision medicine therapies for patients with cancer by using mutation clusters to identify druggable pockets. With a platform that utilizes insights from genomics, computational chemistry, proteomics and AI, Nested is working to reach untapped mutations with the potential to improve outcomes of patients.
Product Description: NST-628
NST-628 is a fully brain-penetrant, mechanistically novel non-degrading molecular glue that targets multiple nodes in the RAS/MAPK pathway. NST-628 was developed based on Nested's proprietary structural insights of how signaling complexes form and function in cancer and addresses common pitfalls of other MAPK-targeted compounds, which remain unable to circumvent the risk of resistance via signaling pathway reactivation. It is currently being evaluated in Phase I for the treatment of Solid tumors.
4. Company Overview: Nurix Therapeutics
Nurix Therapeutics, Inc. is a biopharmaceutical company focused on developing novel therapies that control protein levels by harnessing the body's natural process of ubiquitination. Founded in 2009 and based in San Francisco, Nurix is led by President and CEO Arthur T. Sands, M.D., Ph.D., who previously co-founded Lexicon Pharmaceuticals.
Product Description: NX-2127
NX-2127 is an orally bioavailable protein degrader molecule. It reduces levels of both Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) and the IKZF transcription factors Ikaros (IKZF1) and Aiolos (IKZF3) through targeted ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. NX-2127 acts as a dual PROTAC (through recruitment of cereblon) and molecular glue (degradation of the neosubstrate transcription factors). It is predicted that this approach can achieve clinical efficacy, even in the presence of BTK mutations that confer resistance to clinically used kinase inhibitor drugs. It is currently being evaluated in Phase I for the treatment of B-cell malignancies.
5. Company Overview: Plexium
Plexium is an innovative biotechnology company focused on targeted protein degradation (TPD) to develop novel small molecule drugs for treating various diseases, including cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. Founded in 2017 and based in San Diego, Plexium employs a proprietary drug discovery platform that utilizes high-throughput screening to identify compounds capable of selectively degrading disease-causing proteins. This approach aims to overcome the limitations of traditional therapies, enhancing the efficacy of treatments.
Product Description: PLX-4545
PLX-4545 is designed to destabilize highly suppressive regulatory T cells (Tregs) by inducing the degradation of IKZF2. This mechanism aims to convert Tregs into effector-like T cells, potentially enhancing the immune response against tumors. The drug is administered orally and has shown promising preclinical efficacy, comparable to pembrolizumab, particularly when combined with checkpoint inhibitors.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Executive Summary
Molecular Glues: Overview
- Introduction
- Classification
- Mechanism of action
- Targets
- Application
Molecular Glues -Analytical Perspective: In-depth Commercial Assessment
- Molecular Glues Collaboration Analysis by Companies
Competitive Landscape
- Comparative Assessment of Companies (by therapy, development stage, and technology)
Therapeutic Assessment
- Assessment by Product Type
- Assessment by Stage and Product Type
- Assessment by Route of Administration
- Assessment by Stage and Route of Administration
- Assessment by Molecule Type
- Assessment by Stage and Molecule Type
Molecular Glues: Company and Product Profiles (Marketed Therapies)
Bristol Myers Squibb
- Company Overview
REVLIMID
- Product Description
- Research and Development Activities
- Product Developmental Activities
Molecular Glues: Company and Product Profiles (Pipeline Therapies)
Late Stage Products (Phase III)
- Comparative Analysis
Bristol Myers Squibb
- Company Overview
Golcadomide
- Product Description
- Research and Development Activities
- Product Developmental Activities
Mid Stage Products (Phase II)
- Comparative Analysis
Company Name
- Company Overview
Product Name
- Product Description
- Research and Development Activities
- Product Developmental Activities
Early Stage Products (Phase I)
- Comparative Analysis
Nested Therapeutics
- Company Overview
NST-628
- Product Description
- Research and Development Activities
- Product Developmental Activities
Preclinical and Discovery Stage Products
- Comparative Analysis
Company Name
- Company Overview
Product Name
- Product Description
- Research and Development Activities
- Product Developmental Activities
Inactive Products
- Comparative Analysis