|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1808104
宇宙用バッテリー市場- 世界および地域別分析:プラットフォーム別、バッテリータイプ別、出力別、地域別 - 分析と予測(2025年~2035年)Space Battery Market - A Global and Regional Analysis: Focus on Platform, Battery Type, Power, and Country Level Analysis - Analysis and Forecast, 2025-2035 |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
|
|||||||
| 宇宙用バッテリー市場- 世界および地域別分析:プラットフォーム別、バッテリータイプ別、出力別、地域別 - 分析と予測(2025年~2035年) |
|
出版日: 2025年09月10日
発行: BIS Research
ページ情報: 英文 149 Pages
納期: 1~5営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 図表
- 目次
宇宙用バッテリー市場は、衛星、軌道移動体、ロケット、宇宙ステーションに信頼性の高いミッションクリティカルなエネルギー貯蔵を提供することで、宇宙活動の新しい波に電力を供給する上で極めて重要な役割を果たしています。
バッテリーは、太陽バッテリーアレイが展開するまでの日食期間をつなぎ、マヌーバや観測機器の運用といった需要の高いイベントをサポートし、太陽光が断続的であったり利用できなかったりする長期ミッションの継続性を確保するなど、ミッションのライフサイクル全体にわたって不可欠なものです。打ち上げ間隔が延び、ミッション・アーキテクチャがより野心的になるにつれて、市場はより安全で、より軽量で、より高エネルギーのソリューションへとシフトしています。今日の宇宙空間では、スマートなモジュール式パック設計と、信頼性を高め、耐用年数を延ばすAI対応バッテリー管理システムによって補完された、固体化学とリチウム硫黄化学の急速な進歩が見られます。
| 主要市場統計 | |
|---|---|
| 予測期間 | 2025年~2035年 |
| 2025年の評価 | 8億8,660万米ドル |
| 2035年の予測 | 14億1,810万米ドル |
| CAGR | 4.81% |
市場イントロダクション
世界の宇宙用バッテリーの市場規模は、2024年に8億5,180万米ドルとなりました。現実的なシナリオでは、2035年には14億1,810万米ドルに達すると予測され、予測期間中のCAGRは4.81%です。成長は、商業、民間、防衛の各用途での衛星配備の急増、質量を削減しながらエネルギー密度を高める技術の進歩、軌道上での安全性、可用性、保守性を向上させるAI主導の診断の採用に支えられています。衛星運用会社、宇宙機関、インテグレーター、バッテリー・サプライヤーが一体となって、宇宙バッテリーの役割を受動的な電力リザーバーから、放射線が多く、熱的に不安定な環境でのミッションの成功を支える能動的に管理され、ソフトウェアで定義されたサブシステムへと拡大しています。
プラットフォーム・ミックスは幅広く、高度化が進んでいます。人工衛星は依然として主要な需要の中心であり、地球低軌道コンステレーションに力強い勢いがあり、GEOや深宇宙資産のための電力密度の高いシステムが重視されるようになっています。軌道上輸送機と宇宙物流プラットフォームは、電気推進と効果的に組み合わされる高出力、高速サイクル・バッテリーのニーズを喚起しています。宇宙ステーションやオーバー・ザ・ホライズン持続型月面インフラは、長寿命で耐障害性のあるパックと高度な熱制御に対する要求を後押ししています。このような分野全体では、資格認定とプラットフォーム固有のカスタマイズが依然として決定的であり、化学の選択、パックのアーキテクチャ、バッテリー管理戦略の競合を形成しています。
市場への影響
宇宙用バッテリー市場の短期的なインパクトは、広範な環境的成果よりもむしろ、プログラム・ケイデンス、プラットフォーム性能、資格認定の経済性において最も顕著に現れるであろう。エネルギー密度の向上とパックのモジュール化により、衛星、軌道上輸送機、宇宙ステーション、ロケットなどの主要プラットフォームで使用可能な電力マージンが拡大し、事業者はバスを再設計することなく、より多くのペイロードを搭載したり、デューティサイクルを延長したり、新しいミッションサービスを追加したりできるようになります。これは、電気推進の利用が拡大するにつれて、コンステレーション構築の迅速化、軌道上でのコミッショニングの円滑化、OTVの操縦権限の拡大につながります。
化学およびシステムレベルでの進歩は、調達チームがPDR/CDRで評価するコスト/性能のエンベロープを再構築しています。ソリッドステートとリチウム硫黄のロードマップは、比エネルギーと虐待耐性の段階的変化を約束する一方、次世代リチウムイオンが近い将来の飛行の主力となり続ける。インテグレーターにとって、このことは、より厳しい質量と熱予算、より単純なハーネス、一度認定されれば複数のSKUやパワークラスで再利用できるパック構成をもたらします。
同時に、輸出規制と重要鉱物政策がセル、セパレータ、電子機器の調達を形成し、地域ごとの製造対購入の決定に影響を与え、再設計なしで複数の規制ベースライン(ITAR/ECSS)の認証を取得できるベンダーが有利になります。民間資本(新しいLEO/GEOシステム、月面インフラ、深宇宙探査機)が加速する中、バイヤーは、認定ゲートを満たしながら生産規模を拡大できるプラットフォームとサプライヤーを優先しており、バッテリー技術の選択、パックのモジュール性、認証の信頼性が、受賞とスケジュールリスク軽減の決め手となっています。
産業への影響
宇宙用バッテリー市場は、世界のサプライチェーンの大幅な再構成を推進しています。バリューチェーンは、原材料(リチウム、ニッケル、コバルト、マンガン、グラファイト、セパレータフォイル)から、セルやコンポーネントの製造、モジュール/システムの統合、配備、そして最終的には使用済みリサイクルにまで及ぶ。BIS調査の推計によると、原材料は価値のおよそ15~25%、セルと部品は25~35%、モジュールとシステム統合は20~30%、配備は10~20%、リサイクルは5~15%です。この分布は、上流の採掘・加工の資本集約度と、軌道上でのサービスや回収といった下流サービスの重要性の高まりを反映しています。
産業投資は複数のノードにまたがって拡大しています。北米と欧州は高純度リチウムと正極処理に注力し、日本と南米はセパレーター、負極、特殊電解質に強みを維持しています。統合分野、特に衛星、OTV、月面インフラ用では、宇宙資格認定で実績のある企業(GSユアサ、Saft Groupe、EnerSys、EaglePicher)を中心に統合が進んでいます。リサイクルと循環型経済のアプローチはまだ始まったばかりだが、宇宙空間に焦点を当てた二次鉱物回収や、地上と宇宙のハイブリッド・リサイクル・ループなどの取り組みが注目を集めており、量が増えるにつれて拡大することが予想されます。これらの産業シフトを総合すると、宇宙用バッテリーセクターの戦略的性質が強化され、国家の鉱物安全保障、先進的製造業、長期的持続可能性が結び付けられます。
産業と技術の概要
3つの技術ベクトルが市場の軌道を形成しています。第一に、固体バッテリーが将来の重要なソリューションとして台頭してきており、安全性の向上、エネルギー密度の向上、サイクル寿命の延長を実現しています。その採用はまだプロトタイプに限られていますが、2030年代初頭までには規模が拡大すると予想されます。第二に、スマート・モジュラー・バッテリー・システムは、ミッションに特化したカスタマイズを可能にしています。モジュール式の統合は、NRE(非経常エンジニアリング)コストを削減し、認定サイクルを短縮し、衛星やOTVでのプラグアンドプレイ交換をサポートし、応答性の高い宇宙やメガコンステレーションの需要に沿う。第三に、AIを活用したバッテリー管理システム(BMS)が信頼性を変革しています。センサー・フュージョン、デジタル・ツイン、予知保全を活用することで、これらのBMSは故障の予測、熱負荷の管理、ミッション寿命の延長を可能にし、バッテリーを受動的なサブシステムからインテリジェントなソフトウェア定義の資産へと移行させる。
規制と研究開発の枠組みは、こうした動向をさらに強化します。NASA、ESA、JAXAなどの機関は、熱暴走防止、冗長性、フェイルセーフ動作に関して、より厳しい認定基準を導入しています。輸出規制(ITAR、ECSS)は、サプライヤーの調達や認証パスに影響を与え、リチウム硫黄、ソリッドステート、ハイブリッド化学の特許は、地上EVやグリッド・ストレージの領域からの業界横断的な波及が拡大していることを示しています。宇宙用バッテリーは、妥協のない安全性と信頼性を維持しながら、最先端のエネルギー密度とモジュール性の要求を満たさなければなりません。
市場セグメンテーション:
セグメンテーション1:プラットフォーム別
- 人工衛星
- 深宇宙ミッション
- 軌道上補給機(OTV)
- 宇宙ステーション
- 打ち上げロケット
宇宙用バッテリー市場をリードする衛星(プラットフォーム別)
人工衛星は宇宙用バッテリーの最大かつ最も信頼できる需要中心であり続け、2024年の6億580万米ドルから2035年には9億6,280万米ドルに拡大します。その優位性は、打ち上げ活動の規模の大きさに起因しています。2035年まで計画されている軌道ミッションの80%以上は、衛星配備に直接関連しています。地球低軌道(LEO)では、ブロードバンド接続、地球観測、防衛偵察のためのメガ衛星が、何千回もの充放電サイクルに耐えられるモジュール式の高サイクル・バッテリーを必要とします。静止軌道(GEO)では、高度な通信中継器や高スループット衛星など、ペイロードの高度化が進み、より高いエネルギー密度と冗長性を備えたパックが求められています。
キューブサットから巨大なGEOプラットフォームまで、衛星市場が多様化するにつれ、宇宙用バッテリーは耐障害性、モジュール性、数百回の食サイクルに耐える認定を提供する必要があります。スマートBMSシステム、熱遮蔽、モジュール式パック設計は必須条件となりつつあります。このような継続的な需要により、衛星は当面主要なプラットフォーム・セグメントであり続け、サプライヤの収益を確保すると同時に、OTV、ステーション、深宇宙ミッションへの技術革新を推進します。
セグメンテーション2:バッテリータイプ別
- リチウムバッテリー
- 銀-亜鉛バッテリー
- ニッケルバッテリー
- その他
宇宙用バッテリー市場を独占するリチウム系バッテリー(バッテリータイプ別)
リチウム系バッテリーが引き続き市場シェアの大半を占め、2024年の7億7,610万米ドルから2035年には13億790万米ドルに増加します。リチウムバッテリーの成功は、その優れたエネルギー密度、軽量化、モジュラーパック設計への適応性にあります。ニッケル-水素やニッケル-カドミウムのシステムは、まだ一握りの長期的なプログラムに限られているのとは異なり、リチウム化学は、今日の高スループットのコンステレーションで必要とされる性能とスケーラビリティをサポートしています。
固体リチウムやリチウム-硫黄(Li-S)のような将来の誘導体は、安全性を向上させ、可燃性液体電解質を排除し、大幅な質量削減を提供することにより、このセグメントの優位性を拡大することが期待されています。ニッケルベースの化学物質は実証済みの堅牢性を提供し、数十年にわたり順調に飛行してきたが、バルクとサイクルの制限により競合力が低下しています。リチウムバッテリーは、スマート・モジュラー・システムに統合でき、予測可能なAI主導のBMSを活用できることから、2025~2035年の予測期間を通じて宇宙用電源の基幹であり続け、絶対規模でもミッション・クリティカル・アプリケーションのシェアでも拡大します。
セグメンテーション3:出力別
- 1kW未満
- 1~10 kW
- 11~100 kW
- 100kW以上
- 宇宙用バッテリー市場をリードする1~10kWセグメント(出力別)
定格出力1~10kWの宇宙用バッテリーが主流となり、北米では2024年の4億2,680万米ドルから2035年には6億9,910万米ドルに成長すると予測されます。このセグメントは、衛星、OTV、小型宇宙ステーションのニーズに密接に合致しており、過度の熱蓄積なしに持続的な放電が可能なコンパクトでエネルギー密度の高いパックを必要とします。1~10 kWのシステムが提供するバランスは、推進アシスト、通信、ペイロードの運用をサポートするのに十分な高さでありながら、適格性を維持するのに十分な低さであり、業界の主力製品となっています。
ペイロードとミッションの複雑さが増すにつれて、11~100kWおよび100kW超のセグメントの需要は、特に月面居住施設、大型軌道プラットフォーム、重量のあるOTV向けに加速します。しかし、1~10kWのレンジは、コンステレーション展開や戦術的ミッションの基幹であり続けると予想されます。その拡張性、信頼性、比較的簡単な認定という組み合わせにより、このパワークラスが2035年まで数量と市場全体の価値の両面で支配的であり続けることは確実です。
セグメンテーション4:地域別
- 北米
- 欧州
- アジア太平洋
- その他の地域
北米が宇宙用バッテリー市場をリード(地域別)
北米は、2024年の7億1,050万米ドルから2035年には11億7,470万米ドルに拡大し、地域のリーダーシップを維持すると予想されます。米国は、NASAのArtemisプログラム、国防総省の衛星イニシアティブ、SpaceX、Blue Origin、Northrop Grummanなどの企業が主導する急成長中の商業打ち上げセクターを通じて、この優位性を支えています。GSユアサ、Saftグループ(米国子会社経由)、EnerSys、EaglePicher Technologiesといった大手サプライヤーの存在は、産業基盤をさらに強化しています。
強固な研究開発インフラに加え、北米は認定施設、重要鉱物供給戦略、サプライチェーンリスクを軽減する官民パートナーシップの恩恵を受けています。欧州はESAのもと、ソリッドステートとモジュール設計に多額の投資を行っており、アジア太平洋諸国(中国、インド、日本)は急速に生産能力と国産能力を拡大しています。それでも北米は、飛行遺産と商業化の両方のハブであり続け、予測期間を通じて最大の地域市場シェアを維持しています。
需要:促進要因、限界、機会
市場促進要因:衛星コンステレーション、ディープスペースへの意欲、技術の進歩
宇宙用バッテリー市場は衛星打ち上げの急増に後押しされており、地球低軌道コンステレーションだけでも2025年には50%以上の成長が予測されています。このような前例のない連続性は、迅速な認定と長いサイクル耐久性を備えた耐障害性の高いモジュール式パックを必要とします。同時に、月面基地、火星探査、小惑星探査に及ぶ深宇宙探査の野望は、長寿命、高エネルギー密度、耐放射線性を強化した化学物質への需要を強めています。
技術レベルでは、ソリッド・ステート・バッテリーとリチウム硫黄システムが安全性と重量の画期的な改善を約束し、AI対応のBMSが予知保全、デジタル・ツイン、リアルタイムの温度制御を導入します。これらの進歩により、宇宙用バッテリーは単なるエネルギー貯蔵庫ではなく、ミッションの柔軟性と信頼性を高める能動的なイネーブラとなります。これらの促進要因が相まって、イノベーションがオプションではなく必然である市場環境を支えています。
市場の課題:資格認定負担、コスト圧力、供給制約
強い勢いにもかかわらず、この分野は重大な課題に直面しています。すべてのセル、モジュール、パックは、真空、振動、放射線、過酷な熱サイクルの条件下で実証されなければならないです。ニッケル水素パックで報告されたような熱暴走の事故は、複数のフェイルセーフ、冗長性、保守的な設計マージンの必要性を強めており、これらすべてがコストと重量を押し上げています。
経済的な障壁も同様に困難です。開発・認定キャンペーンには数,000万米ドルの費用がかかることが多く、参加者は主に既存の航空宇宙プライム企業や特殊サプライヤーに限られています。供給面では、重要な鉱物(リチウム、コバルト、ニッケル、グラファイト)やセパレーターフィルムへの依存が、価格変動、地政学的混乱、ITARやECSSなどの輸出規制体制にプログラムをさらします。こうしたリスクは、プロジェクトの経済性を圧迫するだけでなく、衛星や打上げのスケジュールに波及しかねないスケジュールの不確実性をも生み出します。
市場機会:民間投資、ハイブリッド・エネルギー・システム、リサイクルへの取り組み
このような制約に対抗できるのは、大きなチャンスです。民間投資は、宇宙エネルギー新興企業の新しい波に流れ込んでいます。その例としては、Zeno Power(ラジオアイソトープ支援システム)、Aetherflux(固体プロトタイプ)、Pixxel(統合型衛星エネルギープラットフォーム)などがあります。これらの企業は、安全性、モジュール性、領域横断的統合の限界を押し広げています。
太陽バッテリーアレイ、燃料バッテリー、先進バッテリーを組み合わせたハイブリッド・エネルギー・システムは、月面基地、OTV、長期滞在ステーションの強力なイネーブラーとして台頭しつつあります。これらのシステムは、ミッション・プロファイルを拡張し、単一のエネルギー源への依存を低減します。一方、リサイクルや資源回収プログラムも具体化し始めており、退役した宇宙パックからリチウム、ニッケル、コバルトを抽出することを目的とした取り組みが行われています。循環型経済の目標に沿うことで、これらのプログラムはコストを削減し、材料の安全性を向上させ、宇宙産業の持続可能性を高めます。
これらの需要促進要因・課題・機会が相まって、複雑かつダイナミックな市場を定義しています。技術革新と信頼性、コストと資格の厳格さのバランスを取ることができる利害関係者は、長期的な成長を獲得するための最良の立場に立つことができると思われます。
製品/イノベーション戦略:本レポートは、固体バッテリーとリチウム硫黄バッテリーの急速な進歩に伴い、宇宙用バッテリー化学の進化を明らかにし、パックアーキテクチャ、熱設計、乱用耐性、AI対応BMSが、安全性と寿命を向上させるためにどのように収束しつつあるかを解剖しています。研究開発チームは、これらの知見を活用して、資格認定パスの優先順位付け、材料選択のリスク回避、LEO、GEO、深宇宙におけるプラットフォーム固有の制約に合わせたモジュール設計を行うことができます。
成長/マーケティング戦略:宇宙用バッテリー市場は、衛星コンステレーション、深宇宙ミッション、軌道移動体に対する需要の高まりに後押しされ、着実に拡大しています。各社は、宇宙機関や商業打ち上げプロバイダーと積極的に戦略的パートナーシップを結び、長期供給契約を確保し、事業領域を拡大しています。高エネルギー密度、モジュール性、プラットフォーム固有のカスタマイズを重視した先進的なバッテリーシステムを提供することで、企業は複数のミッション・プロファイルにまたがる需要を獲得することができます。固体化学やリチウム硫黄化学などの技術革新を強調し、実証済みの飛行実績を示すことで、サプライヤーはブランドの信頼性を高め、顧客との関係を強化し、今後の衛星や探査プログラムでより大きなシェアを確保することができます。
競合戦略:当レポートでは、GS Yuasa Corporation、Saft Groupe(TotalEnergies)、EnerSys、EaglePicher Technologiesなど、宇宙用バッテリー市場における主要企業の詳細な分析とプロファイリングを掲載しています。この分析では、各社の製品ポートフォリオ、最近の技術動向、プログラムへの参加、地域市場の強みを明らかにしています。市場力学と競合のポジショニングを徹底的に検証しているため、読者は、これらの企業がどのように互いをベンチマークし、進化するプログラム要件に適応しているかを理解することができます。この競合情勢評価により、企業は戦略を練り直し、化学革新やBMS統合などの分野で差別化の機会を特定し、優先度の高い地域やプラットフォームセグメントで成長を追求するための重要な考察を得ることができます。
目次
エグゼクティブサマリー
第1章 市場:業界展望
- 動向:現状と将来への影響評価
- 安全性と効率性を向上させる固体バッテリー
- スマートモジュラーバッテリーの統合とプラットフォーム固有のカスタマイズ
- AI対応診断機能を備えた高度なバッテリー管理システム(BMS)
- サプライチェーンの概要
- 規制状況
- 研究開発レビュー
- ステークホルダー分析
- 進行中の貿易政策分析
- 市場力学
第2章 用途
- 用途のサマリー
- 宇宙用バッテリー市場(用途別)
- 衛星
- 深宇宙ミッション
- 軌道移転機
- 宇宙ステーション
- 打ち上げロケット
第3章 製品
- 製品のサマリー
- 宇宙用バッテリー市場(バッテリー種類別)
- リチウムベースのバッテリー
- 銀亜鉛バッテリー
- ニッケルベースバッテリー
- その他
- 宇宙用バッテリー市場(電力別)
- 1kW未満
- 1~10kW
- 11~100kW
- 100kW以上
第4章 地域
- 地域サマリー
- 北米
- 欧州
- アジア太平洋
- その他の地域
第5章 市場-競合ベンチマーキングと企業プロファイル
- 今後の見通し
- 地理的評価
- 企業プロファイル
- AAC Clyde Space AB
- Airbus SE
- Berlin Space Technologies GmbH
- Blue Canyon Technologies LLC (RTX Corporation)
- Dragonfly Aerospace
- EaglePicher Technologies, LLC
- EnerSys
- GS Yuasa Corporation
- Ibeos
- Pumpkin Inc.
- Saft Groupe SAS (TotalEnergies SE)
- Space Vector (Fisica Inc.)
- Suzhou Everlight Space Technology Co., Ltd.
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Kanadevia Corporation
第6章 調査手法
List of Figures
- Figure 1: Global Space Battery Market (by Scenario), $Million, 2025, 2030, and 2035
- Figure 2: Global Space Battery Market, 2024-2035
- Figure 3: Top 10 Countries, Global Space Battery Market, $Million, 2024
- Figure 4: Global Market Snapshot, 2024
- Figure 5: Global Space Battery Market, $Million, 2024 and 2035
- Figure 6: Space Battery Market (by Platform), $Million, 2024, 2030, and 2035
- Figure 7: Space Battery Market (by Battery Type), $Million, 2024, 2030, and 2035
- Figure 8: Space Battery Market (by Power), $Million, 2024, 2030, and 2035
- Figure 9: Space Battery Market Segmentation
- Figure 10: Supply Chain Overview
- Figure 11: Value Chain Analysis
- Figure 12: Patent Analysis (by Country and Company), January 2022- July 2025
- Figure 13: Key Factors Boosting Satellite Launch Growth
- Figure 14: Six Pillars of Technological Advancements in Lightweight, High-Density Battery System
- Figure 15: Hybrid Energy Storage Systems Transforming Space Power Solutions
- Figure 16: Global Space Battery Market (by Platform), $Million, 2024, 2030, and 2035
- Figure 17: Global Space Battery Market, Satellites Value, $Million, 2024-2035
- Figure 18: Global Space Battery Market, Deep Space Mission Value, $Million, 2024-2035
- Figure 19: Global Space Battery Market, Orbital Transfer Vehicles Value, $Million, 2024-2035
- Figure 20: Global Space Battery Market, Space Stations Value, $Million, 2024-2035
- Figure 21: Global Space Battery Market, Launch Vehicles Value, $Million, 2024-2035
- Figure 22: Global Space Battery Market, (by Battry Type) Value, $Million, 2024, 2030, and 2035
- Figure 23: Global Space Battery Market, (by Power) Value, $Million, 2024, 2030, and 2035
- Figure 24: Global Space Battery Market, Lithium-Based Battery Value, $Million, 2024-2035
- Figure 25: Global Space Battery Market, Silver-Zinc Battery Value, $Million, 2024-2035
- Figure 26: Global Space Battery Market, Nickel-Based Battery Value, $Million, 2024-2035
- Figure 27: Global Space Battery Market, Other Battery Value, $Million, 2024-2035
- Figure 28: Global Space Battery Market, Less than 1kW Value, $Million, 2024-2035
- Figure 29: Global Space Battery Market, 1-10 kW Value, $Million, 2024-2035
- Figure 30: Global Space Battery Market, 11-100kW Value, $Million, 2024-2035
- Figure 31: Global Space Battery Market, Over 100kW Value, $Million, 2024-2035
- Figure 32: U.S. Space Battery Market, $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Figure 33: Canada Space Battery Market, $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Figure 34: Germany Space Battery Market, $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Figure 35: France Space Battery Market, $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Figure 36: U.K. Space Battery Market, $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Figure 37: Italy Space Battery Market, $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Figure 38: Spain Space Battery Market, $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Figure 39: Rest-of-Europe Space Battery Market, $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Figure 40: China Space Battery Market, $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Figure 41: Japan Space Battery Market, $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Figure 42: South Korea Space Battery Market, $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Figure 43: India Space Battery Market, $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Figure 44: Rest-of-Asia-Pacific Space Battery Market, $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Figure 45: Middle East and Africa Space Battery Market, $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Figure 46: Latin America Space Battery Market, $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Figure 47: Data Triangulation
- Figure 48: Top-Down and Bottom-Up Approach
- Figure 49: Assumptions and Limitations
List of Tables
- Table 1: Market Snapshot
- Table 2: Competitive Landscape Snapshot
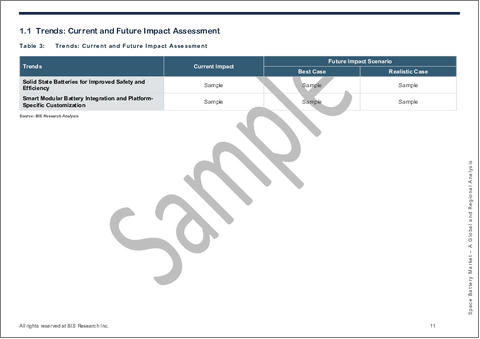
- Table 3: Trends: Current and Future Impact Assessment
- Table 4: Large Scale Grid Storage Deployments
- Table 5: Key Industry Participants and Their Recent Modular Power and Energy Storage Initiatives
- Table 6: Key Industry Players and Recent Battery Management System (BMS) Launches
- Table 7: Regulatory/Certification Bodies in Space Battery Market
- Table 8: Key Operational Use Cases for Space Battery Market
- Table 9: Primary End Users of Space Battery Market and their Operational Focus
- Table 10: Space Battery Procurement Drivers - Core Buying Criteria and Industry Examples
- Table 11: Country/Region Specific Policies in Space Battery Market
- Table 12: Drivers, Challenges, and Opportunities, 2024-2035
- Table 13: Space Battery Market (by Region), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 14: North America Space Battery Market (by Platform), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 15: North America Space Battery Market (by Battery Type), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 16: North America Space Battery Market (by Power), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 17: U.S. Space Battery Market (by Platform), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 18: U.S. Space Battery Market (by Battery Type), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 19: U.S. Space Battery Market (by Power), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 20: Canada Space Battery Market (by Platform), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 21: Canada Space Battery Market (by Battery Type), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 22: Canada Space Battery Market (by Power), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 23: Europe Space Battery Market (by Platform), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 24: Europe Space Battery Market (by Battery Type), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 25: Europe Space Battery Market (by Power), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 26: Germany Space Battery Market (by Platform), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 27: Germany Space Battery Market (by Battery Type), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 28: Germany Space Battery Market (by Power), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 29: France Space Battery Market (by Platform), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 30: France Space Battery Market (by Battery Type), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 31: France Space Battery Market (by Power), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 32: U.K. Space Battery Market (by Platform), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 33: U.K. Space Battery Market (by Battery Type), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 34: U.K. Space Battery Market (by Power), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 35: Italy Space Battery Market (by Platform), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 36: Italy Space Battery Market (by Battery Type), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 37: Italy Space Battery Market (by Power), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 38: Spain Space Battery Market (by Platform), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 39: Spain Space Battery Market (by Battery Type), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 40: Spain Space Battery Market (by Power), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 41: Rest-of-Europe Space Battery Market (by Platform), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 42: Rest-of-Europe Space Battery Market (by Battery Type), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 43: Rest-of-Europe Space Battery Market (by Power), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 44: Asia-Pacific Space Battery Market (by Platform), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 45: Asia-Pacific Space Battery Market (by Battery Type), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 46: Asia-Pacific Space Battery Market (by Power), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 47: China Space Battery Market (by Platform), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 48: China Space Battery Market (by Battery Type), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 49: China Space Battery Market (by Power), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 50: Japan Space Battery Market (by Platform), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 51: Japan Space Battery Market (by Battery Type), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 52: Japan Space Battery Market (by Power), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 53: South Korea Space Battery Market (by Platform), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 54: South Korea Space Battery Market (by Battery Type), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 55: South Korea Space Battery Market (by Power), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 56: India Space Battery Market (by Platform), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 57: India Space Battery Market (by Battery Type), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 58: India Space Battery Market (by Power), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 59: Rest-of-Asia-Pacific Space Battery Market (by Platform), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 60: Rest-of-Asia-Pacific Space Battery Market (by Battery Type), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 61: Rest-of-Asia-Pacific Space Battery Market (by Power), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 62: Rest-of-the-World Space Battery Market (by Platform), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 63: Rest-of-the-World Space Battery Market (by Battery Type), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 64: Rest-of-the-World Space Battery Market (by Power), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 65: Middle East and Africa Space Battery Market (by Platform), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 66: Middle East and Africa Space Battery Market (by Battery Type), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 67: Middle East and Africa Space Battery Market (by Power), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 68: Latin America Space Battery Market (by Platform), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 69: Latin America Space Battery Market (by Battery Type), $Thousand, 2024-2035
- Table 70: Latin America Space Battery Market (by Power), $Thousand, 2024-2035
This report can be delivered within 1 working day.
Introduction to the Space Battery Market
The space battery market plays a pivotal role in powering the new wave of space activity by providing reliable, mission-critical energy storage for satellites, orbital transfer vehicles, launch vehicles, and space stations. Batteries are indispensable across the mission lifecycle; they bridge eclipse periods before solar arrays deploy, support high-demand events such as maneuvers and instrument operations, and ensure continuity on long-duration missions where sunlight is intermittent or unavailable. As launch cadence rises and mission architectures become more ambitious, the market is shifting toward safer, lighter, and higher-energy solutions, space today, with rapid progress in solid-state and lithium-sulfur chemistries, complemented by smart, modular pack designs and AI-enabled battery management systems that raise reliability and extend useful life.
| KEY MARKET STATISTICS | |
|---|---|
| Forecast Period | 2025 - 2035 |
| 2025 Evaluation | $886.6 Million |
| 2035 Forecast | $1,418.1 Million |
| CAGR | 4.81% |
Market Introduction
In 2024, the global space battery market was valued at $851.8 million. Under the realistic scenario, it is projected to reach $1,418.1 million by 2035, reflecting a 4.81% CAGR over the forecast horizon. Growth is anchored in the surge of satellite deployments across commercial, civil, and defense applications; in technology advances that lift energy density while cutting mass; and in the adoption of AI-driven diagnostics that improve safety, availability, and maintainability in orbit. Together, satellite operators, space agencies, integrators, and battery suppliers are expanding the role of space batteries from a passive power reservoir to an actively managed, software-defined subsystem that underwrites mission success in radiation-rich, thermally volatile environments.
The platform mix is broad and increasing in sophistication. Satellites remain the principal demand center, with strong momentum in low Earth orbit constellations and growing emphasis on power-dense systems for GEO and deep-space assets. Orbital transfer vehicles and space logistics platforms are catalyzing needs for high-power, fast-cycling batteries that pair effectively with electric propulsion. Space stations and over-the-horizon sustained lunar infrastructure are driving requirements for long-life, fault-tolerant packs and advanced thermal control. Across this spectrum, qualification rigor and platform-specific customization remain decisive, shaping the competitive playing field for chemistry choices, pack architecture, and battery management strategies.
Market Impact
The space battery market's near-term impact will be most visible in program cadence, platform performance, and qualification economics rather than broad environmental outcomes. Higher energy density and pack modularity are expanding usable power margins across key platforms, i.e., satellites, orbital transfer vehicles, space stations, and launch vehicles, allowing operators to carry more payload, extend duty cycles, or add new mission services without redesigning the bus. This translates into faster constellation build-outs, smoother in-orbit commissioning, and greater maneuver authority for OTVs as electric-propulsion use scales.
Advances at the chemistry and system levels are reshaping the cost/performance envelope that procurement teams evaluate at PDR/CDR. Solid-state and lithium-sulfur roadmaps promise step-changes in specific energy and abuse tolerance, while next-generation Li-ion continues to be the workhorse for near-term flights. For integrators, this yields tighter mass and thermal budgets, simpler harnessing, and pack configurations that can be qualified once and reused across multiple SKUs and power classes.
At the same time, export controls and critical-minerals policies shape sourcing of cells, separators, and electronics, influencing regional make-versus-buy decisions and favoring vendors that can certify to multiple regulatory baselines (ITAR/ECSS) without redesign. As private capital accelerates (new LEO/GEO systems, lunar infrastructure, deep-space probes), buyers are prioritizing platforms and suppliers that can scale production while meeting qualification gates, turning battery technology selection, pack modularity, and certification credibility into decisive factors for award and schedule risk mitigation.
Industrial Impact
The space battery market is driving a deep reconfiguration of the global supply chain. The value chain extends from raw materials (lithium, nickel, cobalt, manganese, graphite, and separator foils), through cell and component manufacturing, to module/system integration, deployment, and ultimately end-of-life recycling. According to BIS Research estimates, raw materials contribute roughly 15-25% of the value, cells and components 25-35%, modules and system integration 20-30%, deployment 10-20%, and recycling 5-15%. This distribution reflects both the capital intensity of upstream mining/processing and the rising importance of downstream services, such as in-orbit servicing and recovery.
Industrial investment is scaling across multiple nodes. North America and Europe are focusing on high-purity lithium and cathode processing, while Japan and South Korea maintain strength in separators, anodes, and specialty electrolytes. The integration segment, particularly for satellites, OTVs, and lunar infrastructure, is consolidating around players with proven space qualification credentials (GS Yuasa, Saft Groupe, EnerSys, EaglePicher). Recycling and circular-economy approaches are still nascent but expected to expand as volumes rise, with initiatives such as space-focused secondary mineral recovery and hybrid terrestrial/space recycling loops gaining attention. Collectively, these industrial shifts reinforce the strategic nature of the space battery sector, linking national mineral security, advanced manufacturing, and long-term sustainability.
Industry and Technology Overview
Three technology vectors are shaping the market trajectory. First, solid-state batteries are emerging as a key future solution, offering improved safety, higher energy density, and longer cycle life, critical in radiation-heavy or thermally volatile orbits. Their adoption remains limited to prototypes but is expected to scale by the early 2030s. Second, smart modular battery systems are enabling mission-specific customization. Modular integration reduces NRE (non-recurring engineering) costs, shortens qualification cycles, and supports plug-and-play replacement in satellites and OTVs, aligning with responsive space and mega-constellation demands. Third, AI-enabled battery management systems (BMS) are transforming reliability. By leveraging sensor fusion, digital twins, and predictive maintenance, these BMS can anticipate failures, manage thermal loads, and extend mission lifetimes, moving the battery from a passive subsystem to an intelligent, software-defined asset.
Regulatory and R&D frameworks further reinforce these trends. Agencies such as NASA, ESA, and JAXA are embedding more stringent qualification standards around thermal runaway prevention, redundancy, and fail-safe operation. Export controls (ITAR, ECSS) influence supplier sourcing and certification paths, while patents in lithium-sulfur, solid-state, and hybrid chemistries indicate growing cross-industry spillover from terrestrial EV and grid storage domains. Collectively, these dynamics underscore a dual imperative; space batteries must meet cutting-edge energy density and modularity demands while maintaining uncompromising safety and reliability.
Market Segmentation:
Segmentation 1: by Platform
- Satellites
- Deep Space Missions
- Orbital Transfer Vehicles (OTVs)
- Space Stations
- Launch Vehicles
Satellites to Lead the Space Battery Market (by Platform)
Satellites remain the largest and most reliable demand center for space batteries, expanding from $605.8 million in 2024 to $962.8 million by 2035. Their dominance stems from the sheer scale of launch activity; more than 80% of planned orbital missions through 2035 are directly tied to satellite deployments. In low Earth orbit (LEO), mega-constellations for broadband connectivity, Earth observation, and defense reconnaissance require modular, high-cycle batteries capable of surviving thousands of charge/discharge cycles. In geostationary orbit (GEO), increasing payload sophistication, including advanced communication transponders and high-throughput satellites, demands packs with greater energy density and redundancy.
As the satellite market diversifies, from CubeSats to massive GEO platforms, space batteries must deliver fault tolerance, modularity, and qualification for hundreds of eclipse cycles. Smart BMS systems, thermal shielding, and modular pack designs are becoming prerequisites. This continuous demand ensures satellites remain the dominant platform segment for the foreseeable future, anchoring revenue for suppliers while driving innovation that later flows into OTVs, stations, and deep-space missions.
Segmentation 2: by Battery Type
- Lithium-Based Batteries
- Silver-Zinc Batteries
- Nickel-Based Batteries
- Others
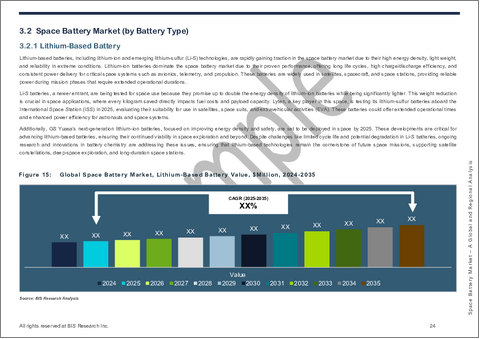
Lithium-Based Batteries to Dominate the Space Battery Market (by Battery Type)
Lithium-based batteries continue to account for the majority of market share, rising from $776.1 million in 2024 to $1,307.9 million by 2035. Their success lies in their superior energy density, lighter mass, and adaptability to modular pack designs. Unlike nickel-hydrogen or nickel-cadmium systems, which remain limited to a handful of long-standing programs, lithium chemistries support the performance and scalability required by today's high-throughput constellations.
Future derivatives such as solid-state lithium and lithium-sulfur (Li-S) are expected to extend the dominance of this segment by improving safety, eliminating flammable liquid electrolytes, and offering substantial mass savings. While nickel-based chemistries provide proven robustness and have flown successfully for decades, their bulk and cycle limitations reduce their competitiveness. Lithium batteries, with their ability to integrate into smart modular systems and leverage predictive AI-driven BMS, will continue to be the backbone of space power through the forecast period 2025-2035, expanding both in absolute scale and in share of mission-critical applications.
Segmentation 3: by Power
- Less than 1 kW
- 1-10 kW
- 11-100 kW
- More than 100 kW
- 1-10 kW Segment to Lead the Space Battery Market (by Power)
Space batteries rated in the 1-10 kW power range are projected to dominate, growing from $426.8 million in 2024 to $699.1 million by 2035 in North America. This segment aligns closely with the needs of satellites, OTVs, and smaller space stations, which require compact, energy-dense packs capable of sustained discharge without excessive thermal buildup. The balance offered by 1-10 kW systems is high enough to support propulsion assists, communications, and payload operations, yet low enough to remain manageable for qualification, making them the workhorse of the industry.
As payloads and mission complexity increase, demand in the 11-100 kW and >100 kW segments will accelerate, particularly for lunar habitats, large orbital platforms, and heavy OTVs. However, the 1-10 kW range is expected to remain the backbone of constellation deployments and tactical missions. Its combination of scalability, reliability, and relatively straightforward qualification will ensure this power class continues to dominate in both unit volume and overall market value through 2035.
Segmentation 4: by Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Rest-of-the-World
North America to Lead the Space Battery Market (by Region)
North America is expected to maintain its regional leadership, expanding from $710.5 million in 2024 to $1,174.7 million by 2035. The U.S. anchors this dominance through NASA's Artemis program, Department of Defense satellite initiatives, and a rapidly growing commercial launch sector led by companies such as SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Northrop Grumman. The presence of leading suppliers such as GS Yuasa, Saft Groupe (via U.S. subsidiaries), EnerSys, and EaglePicher Technologies further strengthens the industrial base.
In addition to robust R&D infrastructure, North America benefits from qualification facilities, critical mineral supply strategies, and public-private partnerships that reduce supply-chain risk. Europe, under ESA, is investing heavily in solid-state and modular designs, while Asia-Pacific nations (China, India, Japan) are rapidly scaling capacity and indigenous capability. Still, North America remains the hub for both flight heritage and commercialization, ensuring it retains the largest regional market share throughout the forecast horizon.
Demand: Drivers, Limitations, and Opportunities
Market Drivers: Satellite Constellations, Deep-Space Ambitions, and Technology Advances
The space battery market is being propelled by a surge in satellite launches, with low Earth orbit constellations alone projected to grow by more than 50% in 2025. This unprecedented cadence requires fault-tolerant, modular packs with rapid qualification and long-cycle durability. Simultaneously, ambitions for deep-space exploration spanning lunar bases, Mars exploration, and asteroid probes are intensifying demand for chemistries with extended lifetimes, high energy density, and enhanced radiation tolerance.
At the technology level, solid-state batteries and lithium-sulfur systems promise game-changing improvements in safety and weight, while AI-enabled BMS introduce predictive maintenance, digital twins, and real-time thermal control. These advances ensure that space batteries are not merely energy reservoirs but active enablers of mission flexibility and reliability. Together, these drivers underpin a market environment where innovation is a necessity, not an option.
Market Challenges: Qualification Burden, Cost Pressures, and Supply Constraints
Despite strong momentum, the sector faces critical challenges. The qualification burden remains extremely high; every cell, module, and pack must be proven under conditions of vacuum, vibration, radiation, and severe thermal cycling. Incidents of thermal runaway, such as those reported with nickel-hydrogen packs, have reinforced the need for multiple fail-safes, redundancy, and conservative design margins, all of which drive cost and weight.
Economic barriers are equally daunting. Development and qualification campaigns often cost tens of millions of dollars, limiting participation primarily to established aerospace primes and specialty suppliers. On the supply side, the reliance on critical minerals (lithium, cobalt, nickel, and graphite) and separator films exposes programs to price volatility, geopolitical disruptions, and export control regimes such as ITAR and ECSS. These risks not only strain project economics but also create scheduling uncertainties that can ripple through satellite and launch timelines.
Market Opportunities: Private Investment, Hybrid Energy Systems, and Recycling Initiatives
Counterbalancing these constraints are significant opportunities. Private investment is flowing into a new wave of space-energy startups, examples include Zeno Power (radioisotope-assisted systems), Aetherflux (solid-state prototypes), and Pixxel (integrated satellite energy platforms). These firms are pushing boundaries on safety, modularity, and cross-domain integration.
Hybrid energy systems, which combine solar arrays, fuel cells, and advanced batteries, are emerging as powerful enablers for lunar bases, OTVs, and long-duration stations. These systems extend mission profiles and reduce dependency on any single energy source. Meanwhile, recycling and resource-recovery programs are beginning to take shape, with initiatives aimed at extracting lithium, nickel, and cobalt from retired space packs. By aligning with circular-economy goals, these programs reduce costs, improve material security, and enhance the sustainability credentials of the space industry.
Together, these demand drivers, challenges, and opportunities define a market that is both complex and dynamic. Stakeholders who can balance innovation with reliability and cost with qualification rigor will be best positioned to capture long-term growth.
How can this report add value to an organization?
Product/Innovation Strategy: This report clarifies the evolution of space-grade battery chemistries, space today, with rapid progress in solid-state and lithium-sulfur batteries, and dissects how pack architecture, thermal design, abuse tolerance, and AI-enabled BMS are converging to raise safety and lifetime. R&D teams can use these insights to prioritize qualification paths, de-risk material choices, and align module designs to platform-specific constraints in LEO, GEO, and deep space.
Growth/Marketing Strategy: The space battery market has been experiencing steady expansion, fueled by the rising demand for satellite constellations, deep-space missions, and orbital transfer vehicles. Companies are actively forming strategic partnerships with space agencies and commercial launch providers to secure long-term supply contracts and expand their operational footprint. By offering advanced battery systems that emphasize high energy density, modularity, and platform-specific customization, organizations can position themselves to capture demand across multiple mission profiles. Emphasizing technological innovation, such as solid-state and lithium-sulfur chemistries, and demonstrating proven flight heritage will allow suppliers to enhance brand credibility, strengthen customer relationships, and secure a larger share of upcoming satellite and exploration programs.
Competitive Strategy: The report provides a detailed analysis and profiling of key players in the space battery market, including GS Yuasa Corporation, Saft Groupe (TotalEnergies), EnerSys, and EaglePicher Technologies. The analysis highlights their product portfolios, recent technological developments, program participation, and regional market strengths. It thoroughly examines market dynamics and competitive positioning, enabling readers to understand how these companies benchmark against each other and adapt to evolving program requirements. This competitive landscape assessment provides organizations with critical insights to refine their strategies, identify differentiation opportunities in areas such as chemistry innovation and BMS integration, and pursue growth in high-priority regions and platform segments.
Research Methodology
Factors for Data Prediction and Modelling
- The base currency considered for the space battery market analysis is US$. Currencies other than the US$ have been converted to the US$ for all statistical calculations, considering the average conversion rate for that particular year.
- The currency conversion rate has been taken from the historical exchange rate of the Oanda website.
- The information rendered in the space battery market report is a result of in-depth primary interviews, surveys, and secondary analysis.
- Where relevant information was not available, proxy indicators and extrapolation were employed.
- Any economic downturn in the future has not been taken into consideration for the market estimation and forecast.
- Technologies currently used are expected to persist through the forecast with no major technological breakthroughs.
Market Estimation and Forecast
The space battery market research study involves the usage of extensive secondary sources, such as certified publications, articles from recognized authors, white papers, annual reports of companies, directories, and major databases to collect useful and effective information for an extensive, technical, market-oriented, and commercial study of the market.
The market engineering process involves the calculation of the market statistics, market size estimation, market forecast, market crackdown, and data triangulation (the methodology for such quantitative data processes has been explained in further sections). The primary research study has been undertaken to gather information and validate the market numbers for segmentation types and industry trends of the key players in the market.
Primary Research
The primary sources involve industry experts from the space battery market and various stakeholders in the ecosystem. Respondents such as CEOs, vice presidents, marketing directors, and technology and innovation directors have been interviewed to obtain and verify both qualitative and quantitative aspects of this research study.
The key data points taken from primary sources include:
- validation and triangulation of all the numbers and graphs
- validation of reports, segmentations, and key qualitative findings
- understanding the competitive landscape
- validation of the numbers of various markets for the market type
- percentage split of individual markets for geographical analysis
Secondary Research
Space battery market research study involves the usage of extensive secondary research, directories, company websites, and annual reports. It also makes use of databases, such as Hoovers, Bloomberg, Businessweek, and Factiva, to collect useful and effective information for an extensive, technical, market-oriented, and commercial study of the global market. In addition to the data sources, the study has been undertaken with the help of other data sources and websites, such as the Space Foundation, UCS, UNOOSA, etc.
Secondary research was done to obtain crucial information about the industry's value chain, revenue models, the market's monetary chain, the total pool of key players, and the current and potential use cases and applications.
The key data points taken from secondary research include:
- segmentations and percentage shares
- data for market value
- key industry trends of the top players in the market
- qualitative insights into various aspects of the market, key trends, and emerging areas of innovation
- quantitative data for mathematical and statistical calculations
Table of Contents
Executive Summary
Scope and Definition
1 Market: Industry Outlook
- 1.1 Trends: Current and Future Impact Assessment
- 1.1.1 Solid State Batteries for Improved Safety and Efficiency
- 1.1.2 Smart Modular Battery Integration and Platform-Specific Customization
- 1.1.3 Advanced Battery Management Systems (BMS) with AI-Enabled Diagnostics
- 1.2 Supply Chain Overview
- 1.2.1 Value Chain Analysis
- 1.3 Regulatory Landscape
- 1.4 Research and Development Review
- 1.4.1 Patent Filing Trend (by Country, and Company)
- 1.5 Stakeholder Analysis
- 1.5.1 Use Case
- 1.5.1.1 Case Study - AstroForge and KULR Technology Group
- 1.5.2 End User and Buying Criteria
- 1.5.1 Use Case
- 1.6 Ongoing Trade Policies Analysis
- 1.7 Market Dynamics
- 1.7.1 Market Drivers
- 1.7.1.1 Increased Global Satellite Launches
- 1.7.1.2 Technological Advancements in Lightweight, High-Density Battery Systems
- 1.7.2 Market Challenges
- 1.7.2.1 Stringent Safety and Reliability Requirements
- 1.7.2.2 High Costs of Development and Deployment
- 1.7.3 Market Opportunities
- 1.7.3.1 Growing Private Sector Investments in Space Technology
- 1.7.3.2 Hybrid Grid Energy Storage Systems
- 1.7.1 Market Drivers
2 Application
- 2.1 Application Summary
- 2.2 Space Battery Market (by Application)
- 2.2.1 Satellites
- 2.2.2 Deep Space Mission
- 2.2.3 Orbital Transfer Vehicles
- 2.2.4 Space Stations
- 2.2.5 Launch Vehicles
3 Products
- 3.1 Product Summary
- 3.2 Space Battery Market (by Battery Type)
- 3.2.1 Lithium-Based Battery
- 3.2.2 Silver-Zinc Battery
- 3.2.3 Nickel-based Battery
- 3.2.4 Others
- 3.3 Space Battery Market (by Power)
- 3.3.1 Less than 1 kW
- 3.3.2 1-10 kW
- 3.3.3 11-100kW
- 3.3.4 Over 100kW
4 Region
- 4.1 Regional Summary
- 4.2 North America
- 4.2.1 Regional Overview
- 4.2.2 Driving Factors for Market Growth
- 4.2.3 Factors Challenging the Market
- 4.2.4 Application
- 4.2.5 Product
- 4.2.6 North America by Country
- 4.2.6.1 U.S.
- 4.2.6.1.1 Application
- 4.2.6.1.2 Product
- 4.2.6.2 Canada
- 4.2.6.2.1 Application
- 4.2.6.2.2 Product
- 4.2.6.1 U.S.
- 4.3 Europe
- 4.3.1 Regional Overview
- 4.3.2 Driving Factors for Market Growth
- 4.3.3 Factors Challenging the Market
- 4.3.4 Application
- 4.3.5 Product
- 4.3.6 Europe by Country
- 4.3.6.1 Germany
- 4.3.6.1.1 Application
- 4.3.6.1.2 Product
- 4.3.6.2 France
- 4.3.6.2.1 Application
- 4.3.6.2.2 Product
- 4.3.6.3 U.K.
- 4.3.6.3.1 Application
- 4.3.6.3.2 Product
- 4.3.6.4 Italy
- 4.3.6.4.1 Application
- 4.3.6.4.2 Product
- 4.3.6.5 Spain
- 4.3.6.5.1 Application
- 4.3.6.5.2 Product
- 4.3.6.6 Rest-of-Europe
- 4.3.6.6.1 Application
- 4.3.6.6.2 Product
- 4.3.6.1 Germany
- 4.4 Asia-Pacific
- 4.4.1 Regional Overview
- 4.4.2 Driving Factors for Market Growth
- 4.4.3 Factors Challenging the Market
- 4.4.4 Application
- 4.4.5 Product
- 4.4.6 Asia-Pacific by Country
- 4.4.6.1 China
- 4.4.6.1.1 Application
- 4.4.6.1.2 Product
- 4.4.6.2 Japan
- 4.4.6.2.1 Application
- 4.4.6.2.2 Product
- 4.4.6.3 South Korea
- 4.4.6.3.1 Application
- 4.4.6.3.2 Product
- 4.4.6.4 India
- 4.4.6.4.1 Application
- 4.4.6.4.2 Product
- 4.4.6.5 Rest-of-Asia-Pacific
- 4.4.6.5.1 Application
- 4.4.6.5.2 Product
- 4.4.6.1 China
- 4.5 Rest-of-the-World
- 4.5.1 Regional Overview
- 4.5.2 Driving Factors for Market Growth
- 4.5.3 Factors Challenging the Market
- 4.5.4 Application
- 4.5.5 Product
- 4.5.6 Rest-of-the-World by Region
- 4.5.6.1 Middle East and Africa
- 4.5.6.1.1 Application
- 4.5.6.1.2 Product
- 4.5.6.2 Latin America
- 4.5.6.2.1 Application
- 4.5.6.2.2 Product
- 4.5.6.1 Middle East and Africa
5 Markets - Competitive Benchmarking & Company Profiles
- 5.1 Next Frontiers
- 5.2 Geographic Assessment
- 5.3 Company Profiles
- 5.3.1 AAC Clyde Space AB
- 5.3.1.1 Overview
- 5.3.1.2 Top Products/Product Portfolio
- 5.3.1.3 Top Competitors
- 5.3.1.4 Target Customers
- 5.3.1.5 Key Personal
- 5.3.1.6 Analyst View
- 5.3.1.7 Market Share, 2024
- 5.3.2 Airbus SE
- 5.3.2.1 Overview
- 5.3.2.2 Top Products/Product Portfolio
- 5.3.2.3 Top Competitors
- 5.3.2.4 Target Customers
- 5.3.2.5 Key Personal
- 5.3.2.6 Analyst View
- 5.3.3 Berlin Space Technologies GmbH
- 5.3.3.1 Overview
- 5.3.3.2 Top Products/Product Portfolio
- 5.3.3.3 Top Competitors
- 5.3.3.4 Target Customers
- 5.3.3.5 Key Personal
- 5.3.3.6 Analyst View
- 5.3.3.7 Market Share, 2024
- 5.3.4 Blue Canyon Technologies LLC (RTX Corporation)
- 5.3.4.1 Overview
- 5.3.4.2 Top Products/Product Portfolio
- 5.3.4.3 Top Competitors
- 5.3.4.4 Target Customers
- 5.3.4.5 Key Personal
- 5.3.4.6 Analyst View
- 5.3.4.7 Market Share, 2024
- 5.3.5 Dragonfly Aerospace
- 5.3.5.1 Overview
- 5.3.5.2 Top Products/Product Portfolio
- 5.3.5.3 Top Competitors
- 5.3.5.4 Target Customers
- 5.3.5.5 Key Personal
- 5.3.5.6 Analyst View
- 5.3.5.7 Market Share, 2024
- 5.3.6 EaglePicher Technologies, LLC
- 5.3.6.1 Overview
- 5.3.6.2 Top Products/Product Portfolio
- 5.3.6.3 Top Competitors
- 5.3.6.4 Target Customers
- 5.3.6.5 Key Personal
- 5.3.6.6 Analyst View
- 5.3.6.7 Market Share, 2024
- 5.3.7 EnerSys
- 5.3.7.1 Overview
- 5.3.7.2 Top Products/Product Portfolio
- 5.3.7.3 Top Competitors
- 5.3.7.4 Target Customers
- 5.3.7.5 Key Personal
- 5.3.7.6 Analyst View
- 5.3.7.7 Market Share, 2024
- 5.3.8 GS Yuasa Corporation
- 5.3.8.1 Overview
- 5.3.8.2 Top Products/Product Portfolio
- 5.3.8.3 Top Competitors
- 5.3.8.4 Target Customers
- 5.3.8.5 Key Personal
- 5.3.8.6 Analyst View
- 5.3.8.7 Market Share, 2024
- 5.3.9 Ibeos
- 5.3.9.1 Overview
- 5.3.9.2 Top Products/Product Portfolio
- 5.3.9.3 Top Competitors
- 5.3.9.4 Target Customers
- 5.3.9.5 Key Personal
- 5.3.9.6 Analyst View
- 5.3.9.7 Market Share, 2024
- 5.3.10 Pumpkin Inc.
- 5.3.10.1 Overview
- 5.3.10.2 Top Products/Product Portfolio
- 5.3.10.3 Top Competitors
- 5.3.10.4 Target Customers
- 5.3.10.5 Key Personal
- 5.3.10.6 Analyst View
- 5.3.10.7 Market Share, 2024
- 5.3.11 Saft Groupe SAS (TotalEnergies SE)
- 5.3.11.1 Overview
- 5.3.11.2 Top Products/Product Portfolio
- 5.3.11.3 Top Competitors
- 5.3.11.4 Target Customers
- 5.3.11.5 Key Personal
- 5.3.11.6 Analyst View
- 5.3.11.7 Market Share, 2024
- 5.3.12 Space Vector (Fisica Inc.)
- 5.3.12.1 Overview
- 5.3.12.2 Top Products/Product Portfolio
- 5.3.12.3 Top Competitors
- 5.3.12.4 Target Customers
- 5.3.12.5 Key Personal
- 5.3.12.6 Analyst View
- 5.3.12.7 Market Share, 2024
- 5.3.13 Suzhou Everlight Space Technology Co., Ltd.
- 5.3.13.1 Overview
- 5.3.13.2 Top Products/Product Portfolio
- 5.3.13.3 Top Competitors
- 5.3.13.4 Target Customers
- 5.3.13.5 Key Personal
- 5.3.13.6 Analyst View
- 5.3.13.7 Market Share, 2024
- 5.3.14 Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- 5.3.14.1 Overview
- 5.3.14.2 Top Products/Product Portfolio
- 5.3.14.3 Top Competitors
- 5.3.14.4 Target Customers
- 5.3.14.5 Key Personal
- 5.3.14.6 Analyst View
- 5.3.14.7 Market Share, 2024
- 5.3.15 Kanadevia Corporation
- 5.3.15.1 Overview
- 5.3.15.2 Top Products/Product Portfolio
- 5.3.15.3 Top Competitors
- 5.3.15.4 Target Customers
- 5.3.15.5 Key Personal
- 5.3.15.6 Analyst View
- 5.3.15.7 Market Share, 2024
- 5.3.1 AAC Clyde Space AB
6 Research Methodology
- 6.1 Data Sources
- 6.1.1 Primary Data Sources
- 6.1.2 Secondary Data Sources
- 6.1.3 Data Triangulation
- 6.2 Market Estimation and Forecast