
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1706590
ネットワーク中心の戦いの世界市場:2025年~2035年Global Network Centric Warfare Market 2025-2035 |
||||||
|
|||||||
| ネットワーク中心の戦いの世界市場:2025年~2035年 |
|
出版日: 2025年04月16日
発行: Aviation & Defense Market Reports (A&D)
ページ情報: 英文 150+ Pages
納期: 3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 図表
- 目次
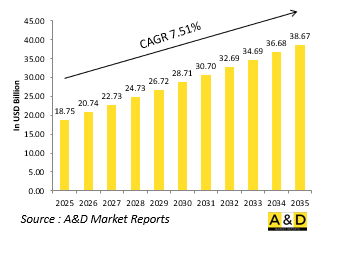
世界のネットワーク中心の戦いの市場規模は、2025年に187億5,000万米ドルと推定され、2035年までに386億7,000万米ドルに成長すると予測されており、予測期間の2025年~2035年の年間平均成長率(CAGR)は7.51%となる見込みです。
ネットワーク中心の戦い市場のイントロダクション:
ネットワーク中心の戦い(NCW)は、戦術的・戦略的優位を得るために情報の優位性を活用することを中心とした、軍事ドクトリンの変革的転換を意味します。センサー、通信ネットワーク、指揮システム、戦闘部隊をシームレスに統合し、まとまりのある、即応性のある、リアルタイムの作戦環境を構築します。NCWの核心は、情報を戦闘力に変えることであり、射撃手、意思決定者、情報資産を領域横断的に結びつけ、状況認識の強化、作戦の同期化、意思決定サイクルの高速化を実現することです。
従来の指揮統制構造は、分散型の意思決定と協調的な対応を可能にするデジタル的に相互接続されたシステムに取って代わられようとしています。この枠組みにより、軍隊は、特にダイナミックで複雑な戦闘地域において、より高い敏捷性、正確性、適応性をもって活動することができます。ネットワーク中心の戦いは、空やサイバーの領域にとどまらず、地上、海上、宇宙、そして統合軍の環境にまで広がり、リアルタイムで努力を統合し、戦場のダイナミクスを再構築します。脅威が混在し、分散し、技術的に洗練されている今日のマルチドメイン紛争では、情報支配力を獲得し、戦力増強を可能にするために、NCWが不可欠です。リアルタイムのUAVフィードから衛星通信リレーに至るまで、世界な防衛風景は、同盟ユニット間の情報共有の深さと速度によってますます定義されるようになっています。
ネットワーク中心の戦い市場における技術の影響:
NCWを支える技術環境は急速に進歩し、現代の軍隊が作戦を計画・実行する方法を根本的に変えています。NCWの中核をなすのは、戦術データリンク、衛星ネットワーク、5G/6G機能などの広帯域通信インフラです。これらは、地上部隊、航空資産、司令部のいずれであっても、ネットワーク内のすべてのノード間の中断のない接続性を確保します。人工知能(AI)と機械学習(ML)は、NCWの効率を高める上で重要な役割を果たします。AIアルゴリズムは膨大なデータセットをリアルタイムで処理し、脅威の特定、戦術的対応の提案、あるいは人的介入を最小限に抑えた資産配備の最適化を行うことができます。予測分析はまた、より優れた任務計画とリスク評価を可能にし、指揮官が作戦上の決定に自信を持てるようにします。
無人車両、遠隔センサー、ロボット支援ユニットなどの自律システムの台頭は、ネットワーク化されたアーキテクチャへの依存をさらに強めています。これらのアセットは多くの場合、半独立的に動作しますが、コマンド・ネットワーク内では緊密に統合されたままであるため、同期と応答性を維持するために堅牢で安全なプロトコルが必要となります。サイバーセキュリティと回復力もまた、NCWシステムにとって不可欠な要素となっています。ドクトリン全体がデータの流れとデジタル接続に依存しているため、通信リンクを防御し、データ侵害、妨害電波、サイバー妨害行為から保護することが最も重要です。そのため、量子暗号化、ブロックチェーンで保護された通信、多層的な認証メカニズムが積極的に開発・導入されています。
もうひとつの重要な技術的進歩は、ウェアラブルな戦場ネットワークとスマート兵士システムの統合です。最新の歩兵キットは現在、身体装着型コンピューター、ヘッドアップディスプレイ、バイオセンサー、戦術無線を備えています。これにより、デジタル化された戦闘員が誕生し、機動性と殺傷力を維持しながら、ドローン、車両、司令部とリアルタイムでやりとりできるようになります。
ネットワーク中心の戦い市場の主要促進要因:
NCW能力の世界規模での採用と拡大を後押ししているのは、いくつかの核となる促進要因です。
作戦の複雑化とマルチドメイン戦争により、従来の部隊構造は有効性を失っています。現代の紛争では、意思決定のスピードと、陸、海、空、サイバー、宇宙の各領域にまたがる連携能力が極めて重要です。NCWは、そのような統合された速いペースの作戦を可能にし、低速のレガシー・システムに依存する敵に対して非対称的な優位性を提供します。
地政学的な不安定さと同盟関係の変化も、世界の防衛態勢に影響を与えています。各国が不確実な安全保障環境に直面する中、自国の防衛態勢と同盟軍との相互運用性を高めるためにNCWへの投資を進めています。例えば、NATOは統合運用性と協調指揮システムを重視しており、加盟国の間でNCWの導入が加速しています。
AI、クラウド・コンピューティング、エッジ・プロセッシング、IoTの融合という技術的収束により、NCWに必要なインフラはよりアクセスしやすく、スケーラブルになっています。軍は現在、カスタム軍用グレードのソリューションと統合された既製技術を使用して、弾力性のあるモジュール式のNCWフレームワークを構築し、コストと展開時間を削減することができます。
反乱ネットワーク、サイバー攻撃、ドローン群などの非対称的でハイブリッドな脅威は、NCWの使用をさらに必要とします。従来の軍隊とは異なり、これらの脅威は多くの場合、分散型で機動性があります。これらに対抗するには、脅威インテリジェンスの迅速な発信、柔軟な展開戦略、リアルタイムの脅威の可視化が必要であり、これらはすべてNCWの特徴です。
国防の近代化プログラムは、世界的にデジタル化とコネクティビティに重点を置いています。各国は、指揮系統の再構築、ネットワーク機能を備えたプラットフォームの更新、接続された戦場で活動するための部隊の訓練など、NCWを中心とした取り組みを開始しています。調達の優先順位は、こうしたデジタル・アーキテクチャにシームレスに「プラグイン」できるプラットフォームやシステムへとシフトしています。
最後に、連合軍や多国籍軍の作戦における相互運用性の要件が、NCW技術の標準化と採用を促進しています。合同演習であれ実戦任務であれ、部隊間で共通の作戦映像を共有できることは不可欠であり、NCWはそのような同期のためのバックボーンを提供します。
ネットワーク中心の戦い市場の地域動向:
米国はNCW能力のパイオニアであり、支配的勢力です。米国国防総省は、JADC2(Joint All-Domain Command and Control)のようなプログラムを通じて、陸海空軍、海兵隊、宇宙軍などすべての部隊を統合し、AIや自律型システムでサポートする統合指揮系統を構築することで、戦争の戦い方を変革しています。カナダも同様に、統合作戦をよりよく調整し、北極圏の防衛態勢を強化するためにデジタル指揮能力を進めています。NATOはNCWを集団防衛の重要な手段として受け入れています。欧州諸国は、加盟国をまたいで機能する安全で相互運用可能なコマンド・プラットフォームに投資しています。ドイツの"Digitale Krafte"と英国の"Land Environment Tactical Communication and Information Systems"(LE TacCIS)は陸上部隊をデジタル化し、プラグアンドプレイの指揮環境を構築する努力の一例です。フランス、スウェーデン、ポーランドも、防空、国境監視、遠征作戦にNCWの枠組みを統合しています。
中国は"情報化"の旗印の下、ネットワーク中心能力を積極的に推進しています。人民解放軍(PLA)は、宇宙、サイバー、運動作戦を一体化した統合指揮ネットワークの構築を目指しています。日本と韓国は、C4ISR(指揮、統制、通信、コンピューター、インテリジェンス、監視、偵察)インフラを近代化し、特に地域の緊張の中で、迅速なデータ共有とリアルタイムの脅威への対応を確実なものにしています。オーストラリアは、将来的な戦力構想の一環として統合戦闘管理システムに投資しており、シームレスな統合運用を目指しています。サウジアラビア、アラブ首長国連邦、カタールなどの湾岸諸国は、国内安全保障と戦力投射の両方を強化するため、NCWシステムを急速に導入しています。同地域の調達戦略は、統合防空・ミサイル防衛システムや、装甲・歩兵部隊の戦場デジタル化を重視しています。イスラエルは、特にセンサー・フュージョン、ドローン連携、サイバー対応戦場認識において、NCW配備のリーダーであり続けています。
アフリカでのNCW導入はまだ始まったばかりですが、成長しつつあります。南アフリカ、エジプト、ナイジェリアなどの国々は、基本的なネットワーク中心コンポーネントを採用し、対反乱活動や国境警備活動を調整しています。アフリカ大陸の課題-接続性の低いインフラから限られた予算まで-は、採用のペースを遅らせています。しかし、ドナーが支援する近代化プログラムや地域の安全保障イニシアティブは、NCWの原則を一部の軍部隊に導入しています。
主要なネットワーク中心の戦いプログラム
インドでは、ドローンやミサイルといった先進システムの導入にメディアの注目が集まっています。しかし、インド空軍の飛行隊戦力の低下、海軍の潜水艦不足、陸軍の先進曳光砲システム(ATAGS)の導入遅れなど、世間一般の認識では重大な能力格差が残っています。致命的ですが、あまり目に見えないギャップとして残っているのは、包括的なネットワーク中心の戦い能力に対する陸軍の20年以上にわたる長年の要求です。その中心は、陸上部隊のための統合戦場管理システム(BMS)の実装であり、この必要性は、集中的な注意と解決を要求し続けています。
当レポートでは、世界のネットワーク中心の戦い市場について調査し、10年間のセグメント別市場予測、技術動向、機会分析、企業プロファイル、国別データなどをまとめています。
目次
防衛資産管理ソフトウェア市場レポートの定義
防衛資産管理ソフトウェア市場セグメンテーション
- エンドユーザー別
- 地域別
- プラットフォーム別
今後10年間のネットワーク中心の戦い分析
この章では、10年間のネットワーク中心の戦い分析により、ネットワーク中心の戦いの成長、変化する動向、技術採用の概要、および全体的な市場の魅力の詳細な概要が示されます。
ネットワーク中心の戦いの市場技術
このセグメントでは、この市場に影響を与えると予想される上位10の技術と、これらの技術が市場全体に与える可能性のある影響について説明します。
世界ネットワーク中心の戦い予測
この市場の10年間のネットワーク中心の戦い予測は、上記のセグメント全体で詳細に説明されています。
地域ネットワーク中心の戦いの動向と予測
このセグメントでは、地域におけるネットワーク中心の戦いの動向、促進要因、抑制要因、課題、そして政治、経済、社会、技術といった側面を網羅しています。また、地域別の市場予測とシナリオ分析も詳細に取り上げています。地域分析の最終段階では、主要企業のプロファイリング、サプライヤーの情勢、企業ベンチマークなどについて分析しています。現在の市場規模は、通常のシナリオに基づいて推定されています。
北米
促進要因、抑制要因、課題
PEST
市場予測とシナリオ分析
主要企業
サプライヤー階層の情勢
企業ベンチマーク
欧州
中東
アジア太平洋
南米
ネットワーク中心の戦いに関する国別分析
この章では、この市場における主要な防衛プログラムを取り上げ、この市場で申請された最新のニュースや特許についても解説します。また、国レベルの10年間の市場予測とシナリオ分析についても解説します。
米国
防衛プログラム
最新ニュース
特許
この市場における現在の技術成熟度
市場予測とシナリオ分析
カナダ
イタリア
フランス
ドイツ
オランダ
ベルギー
スペイン
スウェーデン
ギリシャ
オーストラリア
南アフリカ
インド
中国
ロシア
韓国
日本
マレーシア
シンガポール
ブラジル
ネットワーク中心の戦いのための機会マトリックス
ネットワーク中心の戦いに関する専門家の意見レポート
結論
航空・防衛市場レポートについて
List of Tables
- Table 1: 10 Year Market Outlook, 2025-2035
- Table 2: Drivers, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 3: Restraints, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 4: Challenges, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 5: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 6: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 7: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 8: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 9: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 10: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 11: Drivers, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 12: Restraints, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 13: Challenges, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 14: Drivers, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 15: Restraints, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 16: Challenges, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 17: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Region, 2025-2035
- Table 18: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Platform, 2025-2035
- Table 19: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Type, 2025-2035
- Table 20: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Region, 2025-2035
- Table 21: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Platform, 2025-2035
- Table 22: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Type, 2025-2035
List of Figures
- Figure 1: Global Network Centric Warfare Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 2: Global Network Centric Warfare Market Forecast, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 3: Global Network Centric Warfare Market Forecast, By Platform, 2025-2035
- Figure 4: Global Network Centric Warfare Market Forecast, By Type, 2025-2035
- Figure 5: North America, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 6: Europe, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 7: Middle East, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 8: APAC, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 9: South America, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 10: United States, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 11: United States, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 12: Canada, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 13: Canada, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 14: Italy, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 15: Italy, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 16: France, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 17: France, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 18: Germany, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 19: Germany, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 20: Netherlands, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 21: Netherlands, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 22: Belgium, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 23: Belgium, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 24: Spain, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 25: Spain, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 26: Sweden, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 27: Sweden, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 28: Brazil, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 29: Brazil, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 30: Australia, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 31: Australia, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 32: India, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 33: India, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 34: China, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 35: China, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 36: Saudi Arabia, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 37: Saudi Arabia, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 38: South Korea, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 39: South Korea, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 40: Japan, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 41: Japan, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 42: Malaysia, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 43: Malaysia, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 44: Singapore, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 45: Singapore, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 46: United Kingdom, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 47: United Kingdom, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 48: Opportunity Analysis, Network Centric Warfare Market, By Region (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 49: Opportunity Analysis, Network Centric Warfare Market, By Region (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 50: Opportunity Analysis, Network Centric Warfare Market, By Platform (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 51: Opportunity Analysis, Network Centric Warfare Market, By Platform (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 52: Opportunity Analysis, Network Centric Warfare Market, By Type (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 53: Opportunity Analysis, Network Centric Warfare Market, By Type (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 54: Scenario Analysis, Network Centric Warfare Market, Cumulative Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 55: Scenario Analysis, Network Centric Warfare Market, Global Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 56: Scenario 1, Network Centric Warfare Market, Total Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 57: Scenario 1, Network Centric Warfare Market, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 58: Scenario 1, Network Centric Warfare Market, By Platform, 2025-2035
- Figure 59: Scenario 1, Network Centric Warfare Market, By Type, 2025-2035
- Figure 60: Scenario 2, Network Centric Warfare Market, Total Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 61: Scenario 2, Network Centric Warfare Market, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 62: Scenario 2, Network Centric Warfare Market, By Platform, 2025-2035
- Figure 63: Scenario 2, Network Centric Warfare Market, By Type, 2025-2035
- Figure 64: Company Benchmark, Network Centric Warfare Market, 2025-2035
The Global Network Centric Warfare market is estimated at USD 18.75 billion in 2025, projected to grow to USD 38.67 billion by 2035 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 7.51% over the forecast period 2025-2035.

Introduction to Network Centric Warfare Market:
Network Centric Warfare (NCW) represents a transformative shift in military doctrine, centered on leveraging information superiority to gain a tactical and strategic advantage. It involves the seamless integration of sensors, communication networks, command systems, and combat units into a cohesive, responsive, and real-time operational environment. At its core, NCW is about turning information into combat power-connecting shooters, decision-makers, and intelligence assets across domains to achieve enhanced situational awareness, synchronized operations, and faster decision cycles.
Traditional command-and-control structures are being replaced by digitally interconnected systems that enable distributed decision-making and coordinated responses. This framework allows militaries to operate with greater agility, precision, and adaptability, particularly in dynamic and complex combat theaters. Network centric operations are not confined to air or cyber realms-they extend across ground, sea, space, and joint-forces environments, unifying efforts in real-time and reshaping battlefield dynamics. In today's multi-domain conflicts-where threats are hybrid, dispersed, and technologically sophisticated-NCW is critical for gaining information dominance and enabling force multiplication. From real-time UAV feeds to satellite communication relays, the global defense landscape is increasingly defined by the depth and speed of information sharing among allied units.
Technology Impact in Network Centric Warfare Market:
The technology landscape underpinning NCW has advanced rapidly, fundamentally altering how modern militaries plan and execute operations. At the heart of NCW are high-bandwidth communication infrastructures, including tactical data links, satellite networks, and 5G/6G capabilities. These ensure uninterrupted connectivity between all nodes in the network, whether ground troops, air assets, or command centers. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) play a significant role in enhancing the efficiency of NCW. AI algorithms can process massive datasets in real time, identifying threats, suggesting tactical responses, or optimizing asset deployment with minimal human intervention. Predictive analytics also enables better mission planning and risk assessment, giving commanders more confidence in their operational decisions.
The rise of autonomous systems-such as unmanned vehicles, remote sensors, and robotic support units-has further intensified reliance on networked architecture. These assets often operate semi-independently but remain tightly integrated within the command network, requiring robust and secure protocols to maintain synchronization and responsiveness. Cybersecurity and resilience have also become integral aspects of NCW systems. Since the entire doctrine depends on data flow and digital connectivity, defending communication links and protecting against data breaches, jamming, and cyber sabotage are paramount. As such, quantum encryption, blockchain-secured communications, and multi-layered authentication mechanisms are being actively developed and deployed.
Another key technological advancement is the integration of wearable battlefield networks and smart soldier systems. Modern infantry kits now include body-worn computers, heads-up displays, biosensors, and tactical radios-all of which feed into and extract data from the broader network. This creates a digitized warfighter, capable of interacting with drones, vehicles, and headquarters in real-time while remaining mobile and lethal.
Key Drivers in Network Centric Warfare Market:
Several core drivers are propelling the adoption and expansion of NCW capabilities on a global scale.
Operational complexity and multi-domain warfare have made traditional force structures less effective. In modern conflicts, the speed of decision-making and the ability to coordinate across land, sea, air, cyber, and space domains are crucial. NCW enables that kind of integrated, fast-paced operation, offering an asymmetric advantage over adversaries relying on slower, legacy systems.
Geopolitical instability and shifting alliances are also influencing the global defense posture. As nations face uncertain security environments, they are investing in NCW to boost their defense readiness and interoperability with allied forces. For instance, NATO's emphasis on joint operability and coordinated command systems has accelerated NCW adoption among member states.
Technological convergence-the blending of AI, cloud computing, edge processing, and IoT-has made the infrastructure required for NCW more accessible and scalable. Militaries are now able to build resilient, modular NCW frameworks using off-the-shelf technologies integrated with custom military-grade solutions, reducing cost and deployment time.
Asymmetric and hybrid threats, such as insurgent networks, cyberattacks, and drone swarms, further necessitate the use of NCW. Unlike conventional armies, these threats are often decentralized and mobile. Countering them requires the rapid dissemination of intelligence, flexible deployment strategies, and real-time threat visualization-all hallmarks of NCW.
Defense modernization programs globally are heavily focused on digitization and connectivity. Countries are launching NCW-centric initiatives that restructure command chains, update platforms with networking capabilities, and train forces to operate in a connected battlefield. Procurement priorities are shifting toward platforms and systems that can "plug into" these digital architectures seamlessly.
Lastly, interoperability requirements in coalition and multinational operations are driving standardization and adoption of NCW technologies. Whether in joint exercises or real-world missions, being able to share a common operational picture across forces is essential-and NCW provides the backbone for such synchronization.
Regional Trends in Network Centric Warfare Market:
The United States is the pioneer and dominant force in NCW capabilities. Through programs like Joint All-Domain Command and Control (JADC2), the U.S. Department of Defense is transforming how it fights wars by integrating all branches-Army, Navy, Air Force, Marines, and Space Force-into a unified command structure supported by AI and autonomous systems. Canada is similarly advancing its digital command capabilities to better coordinate joint operations and reinforce Arctic defense postures. NATO has embraced NCW as a critical enabler of collective defense. European nations are investing in secure, interoperable command platforms that can work across member states. Germany's "Digitale Krafte" and the UK's "Land Environment Tactical Communication and Information Systems" (LE TacCIS) are examples of efforts to digitize land forces and create plug-and-play command environments. France, Sweden, and Poland are also integrating NCW frameworks into air defense, border surveillance, and expeditionary operations.
China is aggressively advancing its network-centric capabilities under the banner of "informatization." The People's Liberation Army (PLA) aims to build integrated command networks that unify space, cyber, and kinetic operations. Japan and South Korea are modernizing their C4ISR (Command, Control, Communications, Computers, Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance) infrastructures to ensure rapid data sharing and real-time threat response, especially in the context of regional tensions. Australia is investing in integrated battle management systems as part of its future force initiatives, aiming for seamless joint-service operability. Gulf countries such as Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Qatar are rapidly adopting NCW systems to enhance both internal security and power projection. The region's procurement strategies emphasize integrated air and missile defense systems, as well as battlefield digitization for armored and infantry units. Israel remains a leader in NCW deployment, particularly in sensor fusion, drone coordination, and cyber-enabled battlefield awareness.
NCW implementation in Africa is still nascent but growing. Countries like South Africa, Egypt, and Nigeria are adopting basic network-centric components to coordinate counterinsurgency efforts and border patrol operations. The continent's challenges-ranging from low connectivity infrastructure to limited budget-slow down the pace of adoption. However, donor-backed modernization programs and regional security initiatives are introducing NCW principles into select military units.
Key Network Centric Warfare Program:
In India, media attention has increasingly centered on the induction of advanced systems such as drones and missiles. However, significant capability gaps remain in public perception-such as the Indian Air Force's declining squadron strength, the Navy's shortage of submarines, and the delayed induction of the Army's Advanced Towed Artillery Gun System (ATAGS). One critical yet less visible gap that persists is the Army's long-standing requirement-spanning over two decades-for comprehensive Network Centric Warfare capabilities. Central to this is the implementation of an Integrated Battlefield Management System (BMS) for land forces, a need that continues to demand focused attention and resolution
Table of Contents
Network centric warfare Report Definition
Network Centric Warfare Segmentation
By Region
By Type
By Platform
Network centric warfare Analysis for next 10 Years
The 10-year network centric warfare analysis would give a detailed overview of network centric warfare growth, changing dynamics, technology adoption overviews and the overall market attractiveness is covered in this chapter.
Market Technologies of Network centric warfare
This segment covers the top 10 technologies that is expected to impact this market and the possible implications these technologies would have on the overall market.
Global Network centric warfare Forecast
The 10-year network centric warfare forecast of this market is covered in detailed across the segments which are mentioned above.
Regional Network centric warfare Trends & Forecast
The regional network centric warfare trends, drivers, restraints and Challenges of this market, the Political, Economic, Social and Technology aspects are covered in this segment. The market forecast and scenario analysis across regions are also covered in detailed in this segment. The last part of the regional analysis includes profiling of the key companies, supplier landscape and company benchmarking. The current market size is estimated based on the normal scenario.
North America
Drivers, Restraints and Challenges
PEST
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Key Companies
Supplier Tier Landscape
Company Benchmarking
Europe
Middle East
APAC
South America
Country Analysis of Network centric warfare
This chapter deals with the key defense programs in this market, it also covers the latest news and patents which have been filed in this market. Country level 10 year market forecast and scenario analysis are also covered in this chapter.
US
Defense Programs
Latest News
Patents
Current levels of technology maturation in this market
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Canada
Italy
France
Germany
Netherlands
Belgium
Spain
Sweden
Greece
Australia
South Africa
India
China
Russia
South Korea
Japan
Malaysia
Singapore
Brazil
Opportunity Matrix for Network centric warfare
The opportunity matrix helps the readers understand the high opportunity segments in this market.
Expert Opinions on Network centric warfare Report
Hear from our experts their opinion of the possible analysis for this market.


