
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1858532
極超音速ミサイルの世界市場:2025-2035年Global Hypersonic Missiles Market 2025-2035 |
||||||
|
|||||||
| 極超音速ミサイルの世界市場:2025-2035年 |
|
出版日: 2025年11月01日
発行: Aviation & Defense Market Reports (A&D)
ページ情報: 英文 150+ Pages
納期: 3営業日
|
概要
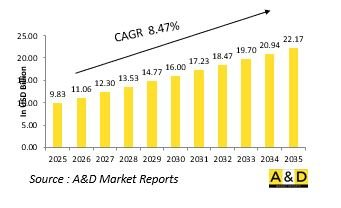
世界の極超音速ミサイルの市場規模は、2025年の98億3,000万米ドルから、予測期間中は8.47%のCAGRで推移し、2035年には221億7,000万米ドルの規模に成長すると予測されています。
極超音速ミサイル市場:イントロダクション
防衛分野における極超音速ミサイル市場は、現代戦において最も変革的な領域の一つとして急速に台頭しており、戦略的抑止力と攻撃能力のバランスを再定義しています。極超音速ミサイルは極めて高速で飛行しながら高い機動性を維持するため、既存の防空システムを回避しつつ高精度の攻撃を実現できます。各国の防衛当局は、これらの兵器システムを抑止および戦力投射の中核資産と位置付けています。極超音速ミサイルは、変化する脅威への迅速な対応と、警告時間を最小限に抑えた戦略的兵器投射を可能にします。市場では現在、防衛機関、航空宇宙企業、研究機関の間で、設計・推進・誘導システムの共同開発が急速に進められています。各国が技術的優位性の確立を競う中、極超音速兵器は次世代の戦争ドクトリンおよび統合防衛戦略の中心的要素となりつつあります。
極超音速ミサイル市場における技術の影響:
技術の進歩は、極超音速ミサイルの速度・精度・生存性を形づくる原動力となっています。特にスクラムジェットやハイブリッドエンジンなどの推進技術の発展により、極高高度での持続的な極超音速飛行が実現しました。さらに、高温・高圧に耐える先端素材の採用により、機体の構造強度と空力効率が大幅に向上しています。また、衛星通信、AI制御、高度アルゴリズムを用いた誘導・航法技術の進化によって、移動目標に対しても高い精度を維持しながら動的に機動する能力を獲得しています。センサーフュージョンや適応型ターゲティング技術は、敵対環境下での攻撃力をさらに高めています。また、高度な指揮統制ネットワークとの統合により、リアルタイムでの任務修正も可能になっています。これらの技術的ブレークスルーにより、極超音速兵器は作戦運用の柔軟性と多用途性を飛躍的に拡大し、将来の打撃および防衛システムの中核的存在として位置づけられています。
極超音速ミサイル市場の主要促進要因:
極超音速ミサイル市場の成長を牽引しているのは、世界的な防衛競争の激化と、戦略的優位性の確保という喫緊のニーズです。各国は、抑止力の強化と新たな脅威への迅速・精密な対応能力を確保するため、極超音速兵器開発を最優先課題に位置づけています。既存のミサイル防衛システムでは極超音速兵器の迎撃が困難であることから、各国は攻撃型・迎撃型の両面における極超音速プログラムへの投資を強化しています。また、長距離精密攻撃能力や時間依存性の高い目標攻撃への需要が、極超音速ミサイル導入をさらに後押ししています。防衛近代化政策や地政学的対立の激化も、各国政府に自国開発の加速を促しています。さらに、共同試験プログラムや官民連携が、推進・熱制御・誘導技術の分野での革新を推進しています。総じて、戦略的緊迫感と技術革新への野心こそが、この市場の成長を支える二大原動力です。
当レポートでは、世界の極超音速ミサイルの市場を調査し、市場背景、市場影響因子の分析、市場規模の推移・予測、各種区分・地域別の詳細分析などをまとめています。
目次
極超音速ミサイル市場:目次
極超音速ミサイル市場:レポートの定義
極超音速ミサイル市場:セグメンテーション
地域別
製品別
ガイダンス別
今後10年間の極超音速ミサイル市場の分析
極超音速ミサイル市場の技術
世界の極超音速ミサイル市場の予測
極超音速ミサイル市場の動向・予測:地域別
調査内容:市場動向、促進要因、制約要因、課題、PEST分析、市場予測、シナリオ分析、主要企業のプロファイル、サプライヤー情勢、企業ベンチマーキング
北米
促進要因、制約、課題
PEST分析
市場予測・シナリオ分析
主要企業
サプライヤー情勢
企業ベンチマーク
欧州
中東
アジア太平洋地域
南米
極超音速ミサイル市場の国別分析
米国
防衛プログラム
最新ニュース
特許
この市場における現在の技術成熟度
市場予測とシナリオ分析
カナダ
イタリア
フランス
ドイツ
オランダ
ベルギー
スペイン
スウェーデン
ギリシャ
オーストラリア
南アフリカ
インド
中国
ロシア
韓国
日本
マレーシア
シンガポール
ブラジル


