
|
年間契約型情報サービス
商品コード
1349830
頭頸部扁平上皮がん(HNSCC)- Tumour DeckHead and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC) - Tumour Deck |
||||||
|
|||||||
| 頭頸部扁平上皮がん(HNSCC)- Tumour Deck |
|
出版日: 年間契約型情報サービス
発行: Mellalta Meets LLP
ページ情報: 英文 300 Pages
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
頭頸部(H&N)がんの主な標的は、口唇粘膜、咽頭、喉頭、副鼻腔などの口腔から発生する腫瘍です。これらの腫瘍の95%以上は扁平上皮がんです。口腔がん、下咽頭がん、喉頭がん、ヒトパピローマウイルス(HPV)非関連中咽頭がんの最も一般的な原因は、タバコとアルコールの使用障害です。頭頸部がん、特にタバコとアルコールによる頭頸部がんの患者は、頭頸部、肺、食道、膀胱、およびこれらの発がん物質に曝された他の部位に、原発性腫瘍が同期して発生し、二次原発性新生物が発生する危険性があります。
転移性頭頸部がんは、特に、通常放射線療法と化学療法を含む前治療で病勢が進行した後の治療が課題です。過去4年間、免疫療法が承認され、2つのPD-1阻害剤が再発転移の治療で承認され、大きな盛り上がりを見せてきました。現在、臨床試験が進行中で、これが最終治療へと移行しつつあります。
頭頸部扁平上皮がんはがん細胞のみで構成されているのではなく、むしろ腫瘍細胞が微小環境の様々な構成要素と相互作用するダイナミックな生態系です。このエコシステムには、免疫細胞、がん関連線維芽細胞(CAF)、がん幹細胞(CSC)、血管系、ヒトパピローマウイルス(HPV)などのウイルス因子が含まれます。これらの構成要素間の相互作用とクロストークを理解することは、効果的な治療戦略を開発するために不可欠です。
進行期腫瘍の発生率が相対的に高いのは、HNSCC腫瘍において早期患者の症状が限定的であること、または早期から進行期への進行が早いことに関連している可能性があります。cN0頸部の最大40%には潜伏転移病変が存在します。したがって、転移を早期に発見するための腫瘍バイオマーカーの開発が不可欠です。腫瘍マーカーは二次予防に重要な役割を果たします。腫瘍マーカーとして生化学的および免疫学的表現を用いて腫瘍の分化を定量化することができます。現在、FDAは28のバイオマーカーをin vitroでの確実な試験を経て臨床使用することを承認しています。しかし、HNSCCの診断や予後のためにFDAが承認したタンパク質や突然変異マーカーはありません。
多剤併用療法を受けた局所進行HNSCC患者の50%以上が、治癒を目的とした治療を終えてから3年以内に再発・転移を起こします。現在、早期発見のための効果的なスクリーニング法がないため、かなりの症例が進行した段階で診断されています。
当レポートでは、世界の頭頸部扁平上皮がん(HNSCC)市場について調査し、市場の現状とともに、症例数の動向、患者動向、競合製品の市場における位置づけ、市場の機会などを提供しています。
目次
第1章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第2章 頭頸部扁平上皮がん(HNSCC)の概要
- 頭頸部扁平上皮がん(HNSCC)の定義、症状、病因、病因
- HNSCCにおける分子変化
第3章 頭頸部扁平上皮がん(HNSCC)の定義と診断
- 診断用バイオマーカー
- 診断アルゴリズム
第4章 頭頸部扁平上皮がん(HNSCC)疫学
- 国別の罹患率
- HNSCCの国別の段階的分類
第5章 頭頸部扁平上皮がん(HNSCC)の治療実践
第6章 頭頸部扁平上皮がん(HNSCC)の承認された標的治療
- 標的療法の概要
- 頭頸部扁平上皮がん(HNSCC)におけるアンメットニーズ
- 病気の再発および/または転移率が高い
- HPV陽性HNSCCとHPV陰性HNSCCの治療戦略に区別はない
- 現在の新たな標的療法の課題
第7章 パイプライン臨床試験
- 頭頸部扁平上皮がん(HNSCC)パイプ情勢の概要と分析
- 分子標的療法の臨床開発
- 臨床試験における主要な分子と結果
- 主要な医薬品の承認と発売のタイムライン
第8章 第III相資産
- 臨床試験と結果
- 第II相資産
- 臨床試験と結果
第9章 第I相資産
- 臨床試験と結果
第10章 頭頸部扁平上皮がん(HNSCC)パイプラインの初期段階分子
第11章 頭頸部扁平上皮がん(HNSCC)パイプラインの非臨床分子
第12章 医師/KOLのインプット
- 米国、EU、日本の4人のKOLからの洞察
- 頭頸部扁平上皮がん(HNSCC)における主要イベント
- 承認された標的療法の拡大
- 新たな実行可能な目標の作成
第13章 頭頸部扁平上皮がん(HNSCC)市場予測-2033年
- 主要薬剤別の市場予測と患者シェア
第14章 付録
Head and Neck (H&N) cancers primarily targets tumors originating from the oral cavity, including the mucosal lip, pharynx, larynx, and paranasal sinuses. More than 95% of these tumors are squamous cell carcinomas. The most common causes for oral cavity, hypopharynx, larynx, and Human Papillomavirus (HPV)-unrelated oropharynx cancers are tobacco and alcohol use disorders. Patients with H&N cancers, particularly those caused by tobacco and alcohol, risk synchronous primary tumors and developing second primary neoplasms in the H&N, lung, esophagus, bladder, and other sites exposed to these carcinogens.
"Metastatic head and neck cancer is a challenging disease to treat particularly after disease progression on prior therapy, which usually includes radiation and chemotherapy. Over the last 4 years, we've seen the big excitement with immunotherapy being approved, with 2 PD-1 inhibitors approved in the recurrent metastatic setting. We're seeing this moving now to the definitive therapy setting with trials that are accruing."
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma is not solely composed of cancer cells but is rather a dynamic ecosystem where tumor cells interact with various components in their microenvironment. This ecosystem includes immune cells, cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), cancer stem cells (CSCs), vasculature, and viral factors such as human papillomavirus (HPV). Understanding the interactions and crosstalk between these components is essential for developing effective treatment strategies.
The relative higher incidence of advanced stage tumours could be related to limited symptomatology in patients with early stage or swift progression from early to advanced stage in HNSCC tumours. Up to 40% of cN0 necks harbor occult metastatic disease. Hence, developing tumour biomarkers to detect metastasis at early stage is essential. Tumour markers play a significant role in secondary prevention. Tumour differentiation can be quantified using biochemical and immunological representation as tumour markers. Currently, the FDA has approved 28 biomarkers after robust in vitro tests for clinical use. However, there is no protein or mutation marker approved for diagnosis or prognosis in HNSCC by the FDA
Mellalta Meets: Predictive Biomarkers of Checkpoint inhibitors
Predictive Biomarkers of Checkpoint inhibitors
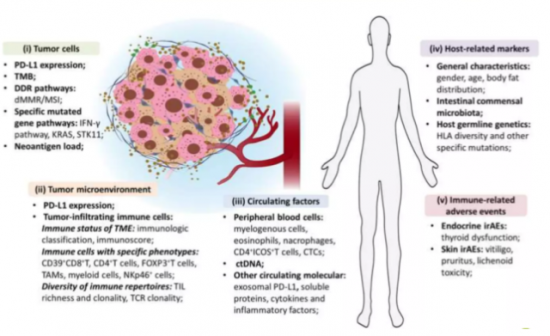
Source: Bai et al, 2020.
Mellalta's Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) Deck: Current Treatment Landscape
The current standard of care for locally advanced (LA) HNSCC and recurrent/metastatic (R/M) HNSCC involves a combination of treatment modalities, including surgery, radiation therapy (RT), and chemotherapy.
For LA HNSCC, the primary treatment modality is often a combination of surgery and RT. In some cases, multimodal approach is considered in which chemotherapy may also be administered concurrently with RT to enhance its effectiveness.
For R/M HNSCC, the treatment options are more limited. Systemic therapy, which includes chemotherapy and targeted therapy, is the mainstay of treatment. Chemotherapy drugs such as cisplatin, carboplatin, and 5-fluorouracil are commonly used. Targeted therapies, such as cetuximab (an anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody), may also be used in combination with chemotherapy.
Immunotherapy has emerged as a promising treatment option for R/M HNSCC. Immune checkpoint inhibitors, such as pembrolizumab and nivolumab, have shown significant efficacy in improving overall survival in patients with R/M HNSCC.
Mellalta Meets Immunotherapies in HNSCC
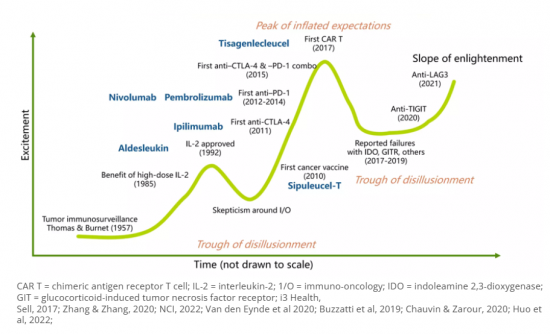
"Management of early-stage locoregional HNSCC primarily rests on a combination of chemotherapy and radiation therapy. However, the therapeutic trajectory becomes intricate for patients experiencing local or regional recurrence due to radiation field overlaps. Additionally, the management of recurrent or second primary HNSCC has become more complex due to the increased incidence of HPV-associated HNSCC compared to non-HPV HNSCC. This change in disease profile has led to a wider range of treatment options available to practicing oncologists, further complicating the decision-making process."
Mellalta's Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) Deck: Current Unmet Needs
- High rate of disease recurrence and/or metastasis and poor treatment outcomes severely affect long term survival: Over 50% of patients with locally advanced HNSCC who receive multimodal approached develop recurrent or metastatic disease within 3 years of the completing curative-intent treatments.
- Early detection of HNSCC is crucial for better treatment outcomes: Currently, there is a lack of effective screening methods for early detection, leading to a significant number of cases being diagnosed at advanced stages.
- No distinction in treatment strategy for HPV-positive and HPV-negative HNSCC which produces significant morbidity: HPV-positive and HPV-negative HNSCC distinctly differ genetically, they are treated in much the same way, an approach that produces significant morbidity. For patients with advanced-stage HPV-positive HNSCC, the 5-year survival rates are 75% to 80%, whereas fewer than 50% of patients with HPV-negative disease survive for 5 years.
- Diverse cases of Potential ICI resistance mechanisms in R/M HNSCC, which necessitates that many molecular targeted agents be tested in combination with ICIs
"Use of immunotherapy in the treatment of [HNSCC] is still evolving, with a continued unmet need for first-line regimens that provide durable clinical benefit with tolerable safety, further research is needed to determine the utility of dual immunotherapy as a treatment option for [HNSCC] and identify novel biomarkers to predict benefit with immunotherapy."
Mellalta's Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) Deck: Key Takeaways
- Radiotherapy plus concomitant chemotherapy for fit patient's with unresected LA SCCHN (stage III-IV) has been shown to improve 5-year absolute survival by 6.5% compared with locoregional treatment alone.
- Despite of Cisplatin-Associated Toxicities, Cisplatin remains the radiosensitizer of choice for the majority of patients with locoregionally advanced head and neck cancer.
- Cetuximab is the only targeted therapy that has been proven effective for the treatment of HNSCC in both the LA and R/M settings. The incorporation of cetuximab not only expanded the range of treatment options in the past decade but also encouraged the investigation of many other targeted therapies in this tumor type.
- The current standard of care (SOC) in the second-line treatment of HNSCC typically results in an ORR of approximately 10-18%. There is room for improvement in the effectiveness of existing treatments.
Mellalta's Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) Deck: Questions Answered:
- How can anti-PD-1/L1 therapies improve outcomes for patients with locally advanced HNSCC? Which combination strategies involving PD1-based therapies can drive change in recurrent/metastatic HNSCC?
- How can Merck Group's IAP antagonist xevinapant change the treatment paradigm for locally advanced HNSCC?
- How do oncologists view the role of Adlai Nortye's anti-PI3K agent buparlisib in the treatment of PD-1-refractory HNSCC?
- What are the key challenges and opportunities in the development of novel therapies for HNSCC, according to KOLs?
- Which companies are best placed to exploit the approach of novel IO-doublet regimens in HNSCC?
Table of Content
1. Executive Summary
- 1.1. Summary of future trends
- 1.2. Potential opportunities to explore.
- 1.3. Drivers/barriers for entry
- 1.4. What's new in HNSCC.
2. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) Overview
- 2.1. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) definition, symptoms, etiology, Pathogenesis
- 2.2. Molecular Alterations in HNSCC
3. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) Definition & Diagnosis
- 3.1. Diagnostic Biomarkers
- 3.2. Diagnostic Algorithm
4. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) Epidemiology
- 4.1. Incidence rates by countries
- 4.2. Stage specific cases of HNSCC by countries
5. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) Treatment Practices
- 5.1. Current treatment practices
- 5.2. Treatment algorithms
- 5.3. Summarized version of NCCN and ESMO treatment guidelines
- 5.4. Acceptable endpoints for accelerated approval?
6. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) Approved Targeted Treatments
- 6.1. Quick overview of targeted therapies
- 6.2. Unmet Needs in Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC)
- 6.3. High rate of disease recurrence and/or metastasis
- 6.4. No distinction in treatment strategy for HPV-positive and HPV-negative HNSCC
- 6.5. Challenges with the Current Emerging Targeted Therapy
- 6.6. To be Continued…
7. Pipeline clinical trials
- 7.1. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) pipeline landscape overview and analysis
- 7.2. Clinical Development of Molecular Targeted Therapy
- 7.3. Key molecules in clinical trials and results
- 7.4. Timeline of key drug approvals and launches.
8. Phase III Assets
- 8.1. Clinical trials and results
- 8.2. Phase II Assets
- 8.3. Clinical trials and results
9. Phase I Assets
- 9.1. Clinical trials and results
10. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) Pipeline Early-Stage Molecules
- 10.1. Phase I and Phase I/II molecules
- 10.2. Mechanism of action, trial dates, and topline results
11. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) Pipeline Non-clinical Molecules
- 11.1. Pre-clinical molecules
- 11.2. Mechanism of action, catalyst dates, and events
12. Physicians/KOLs Input
- 12.1. Insights from 4 KOLs in the US, EU, and Japan
- 12.2. Key Catalyst Events in Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC)
- 12.3. Expansion of approved targeted therapies
- 12.4. Creation of new actionable targets
13. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) Market Forecast -2033
- 13.1. Market Forecast and patient share by key drugs

